
Chassis: Scuderia Ferrari Class: F1 2014 Engine: Ferrari 059/3 1.6L Turbo V6 Fuel: Petrol Transmission:8 speed sequential Brakes: Carbon/Carbon 0 Weight: – Fuel Tank: ATL Year introduced: 2014
 The F14 T is the sixtieth car built by Ferrari specifically to take part in the Formula 1 World Championship. The name comes from the combination of the current year and the introduction of the turbo-compressor in the Power Unit.
The F14 T is the sixtieth car built by Ferrari specifically to take part in the Formula 1 World Championship. The name comes from the combination of the current year and the introduction of the turbo-compressor in the Power Unit.
Although the traditional gestation period for a new Formula 1 design is a little over twelve months, this project, which goes by the internal code name 665, began life more than two years ago. 2014 is an exceptional year in the history of the sport, with a raft of rule changes that commanded an early start to allow the ground up revision of every aspect of the car’s design. To cope with the unprecedented challenge of running three car projects simultaneously during 2012, the Scuderia was fortunate to be able to call on the talents of experienced engineers to guide the project in its early stages.
Followers of the Scuderia will be able to see some of the heritage of earlier Ferrari designs in the F14 T – the obvious areas of continuity are the pull-rod front and rear suspension. However, beyond this superficial similarity there is little to connect the 2014 car to its predecessors.

Externally, the car is very different to the cars of recent years: changes to the regulations to lower the chassis and nose in the interests of driver safety give the F14 T a very different appearance to the F138 and presented the designers with a real challenge to repackage the front suspension into a much lower monocoque. The 2014 rear wing family shares nothing with the previous year owing to three rule changes requiring a much larger stroke DRS, a much smaller overall rear wing depth and removal of the beam wing, thereby requiring the main plane to be supported by central pillars. The front wing is regulated to be 75mm narrower per side in order to make it less vulnerable to collisions with other cars and with the barriers. This change, perhaps one of the less noticeable visual differences to the 2013 cars, has a profound effect on the aerodynamics of the vehicle. The front wings used since 2009 have all featured elaborate measures to encourage the wake of the front wing endplates to pass around the outside of the front tyres in order to maximize the downforce on the car. An innocent change of just 75mm to the position of the wing tip has required us to reinvent completely the front wing aerodynamics for 2014.
Although the external differences are striking, the largest areas of difference occur beneath the skin of the car. The new car has completely different cooling requirements from any of its predecessors. Engine oil and water radiators shrink in size to match the relatively smaller V6 internal combustion part of the Power Unit. However, new homes had to be found to accommodate an intercooler for the turbo-compressor system and to manage heat rejection from ERS components that are many times greater than their KERS antecedents. Given that more cooling allows more horsepower, but more cooling also damages downforce generation it was necessary to decide very carefully on the correct level of overall cooling for the car to render the best lap time compromise between horsepower and downforce. This is one of the key areas where having both Power Unit and Chassis under one roof has been strongly to the benefit of the Scuderia. Having chosen the correct overall level of cooling to supply, packaging the resultant cooler elements and managing the correct airflow to them is something which has absorbed a very large investment of design time to ensure that the F14 T is able to retain the sharply tapered bodywork that allows efficient extraction of downforce from the design.
The braking system has been completely redesigned to adapt the car to the change in the regulations: This has involved ensuring greater capacity on the front axle, while working with Brembo to reduce the size of the hydraulic caliper at the rear to compensate for the greater braking effort that is supplied by the ERS motor. In addition, as permitted by the regulation, the F14 T will have a brake-by-wire system for the first time to allow us to optimize pedal consistency and brake balance control as the ERS braking contribution changes during the braking manoeuvre.
The 2014 Power Units produce greater peak power than their 2013 counterparts and do so at lower RPM with higher torque. Furthermore, the regulations require us to fix a choice of just 8 ratios for the season. This places very different requirements on the transmission than any of the previous generation of Formula 1 cars. The F14 T transmission has been designed with the aim of ensuring that we continue to enjoy highly efficient delivery of power through the drivetrain while producing class leading starts and high levels of reliability.
The sheer complexity of the 2014 regulations produces a layout that is significantly harder to deliver beneath the weight limit (691 kg) than in previous years. Weight control has been an important part of the project from the outset in order to deliver a car with a workable amount of ballast that will permit us to operate and develop the car through the season. Equally important will be the car’s integration with the new tyres that Pirelli is introducing this year. The ability of the F14 T to get the most out of their characteristics will be one of the cornerstones in terms of seeing if our overall efforts will deliver the hoped for results.
INTERVIEWS
TECHNICAL ANALYSIS
The most striking design feature of the F14-T is the nose shape, like all teams Ferrari has had to develop a low nose design of car whilst keeping the chassis as high as possible for aerodynamic reasons. Ferrari’s solution is curious in that it seems to restrict airflow under the nose rather than allow it (such as on the Lotus E22)
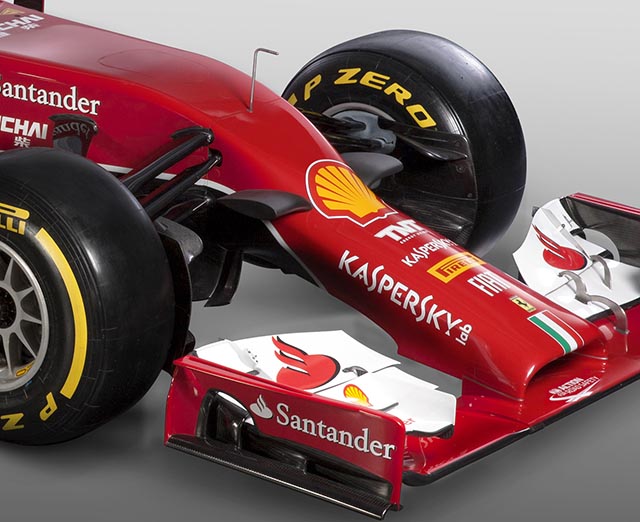

At the front of the car the pull rod suspension is clearly evident, but more interesting is the sculpted camera positions (below), in the past these have been straight edged components but on the F14-T they are a lot more curvy. It seems certain that this is for aerodynamic gain and will likely be copied by other teams, of perhaps even protested. Every car has to run these mounts for the television cameras but most of the time they are a very simple shape.

Above the sidepod duct (below) is a very nicely sculpted turning vane, many cars featured these in 2013 but this is perhaps the most intricate design yet seen. Note the use of spread-tow carbon fibre inside the radiator duct.
Also of interest is the small size of the side pod ducts, the F14-T seems overall to have a surprisingly small amount of cooling. Compare the F14-T (above) with the F138 (below)

This highlights how small the cooling apertures on the F14-T really are, indeed on other 2014 cars we have seen so far the coolers have been larger and various other gills and louvres can be seen on the bodywork.

A look at the front floor and the stay which stops it from flexing too much (below), this is a likely area of development. It maybe that the opening sometimes seen on the F138 in this region may be present on the F14-T to provide additional cooling.

The roll hoop of the F14-T more angular than that of the F138 (below) but apparently similar in size. Note though how the F138 required an additional cooling aperture behind the roll hoop (something also evident on the 2014 Force India), but the F14-T does not have such a feature.

All of this could suggest that the Ferrari 059/3 engine has a lower cooling demand than either the Mercedes or Renault power units. But as this is the only Ferrari powered car seen at this point it is hard to say.

At the rear of the car some additional cooling can be seen, sat on the cars centre line are two vents, the exact purpose of which is unclear. Note also the rear suspension layout and the holes at the rear of the floor.
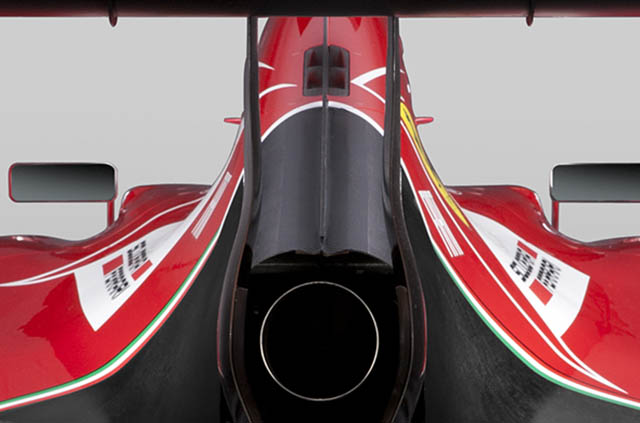
From the rear the extra vents on the centre line are clear to see as is the exhaust exit.
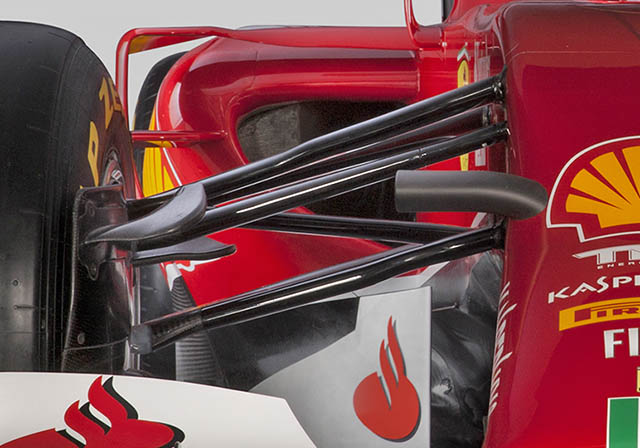
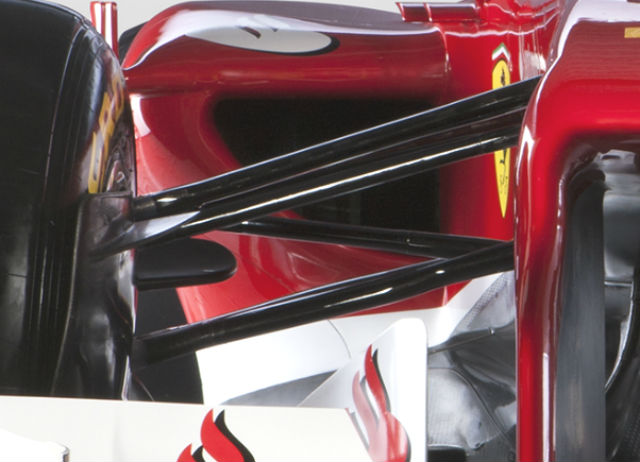
A nice look at the rear suspension, a pull rod layout is retained and the impact of the larger gear casing is evident.
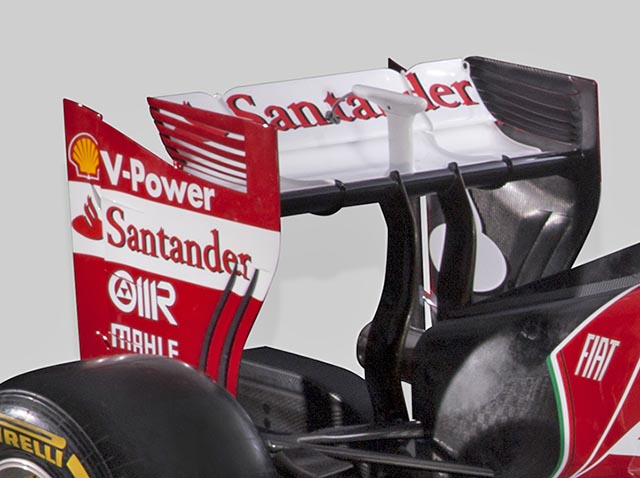

The rear wing carries over many of the details seen on the F138 but the support structure is quite different due to the loss of the lower beam wing. Thermal management on these wing supports will be crucial, as the supports sit right next to the tailpipe. If they fail through heat the result could be rather spectacular.
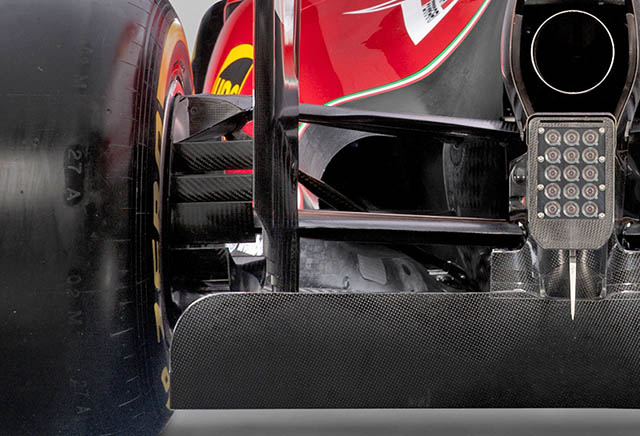

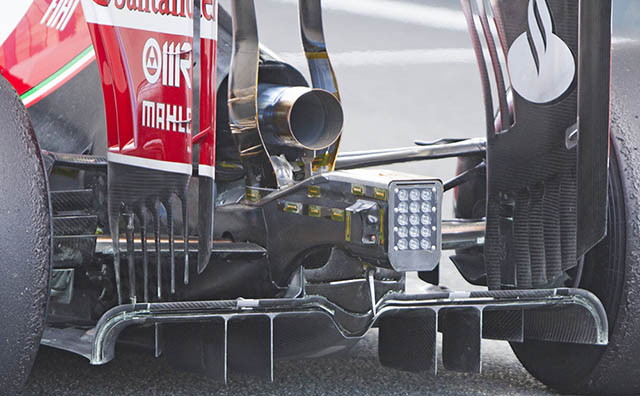
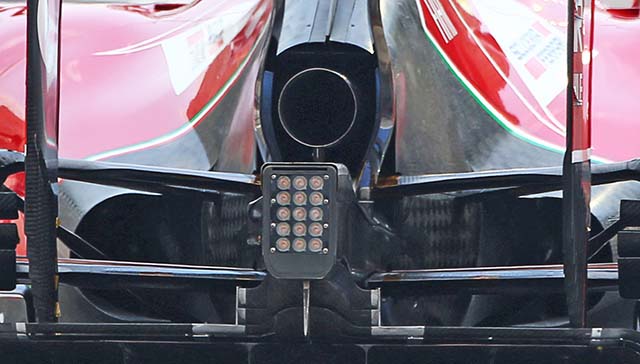
A look at the rear of the car does not show the diffuser as the team covered it for the launch, which is standard practice. But the brake duct winglets, cooling exits and rain light are clear to see.
TEST 01: JEREZ SPAIN
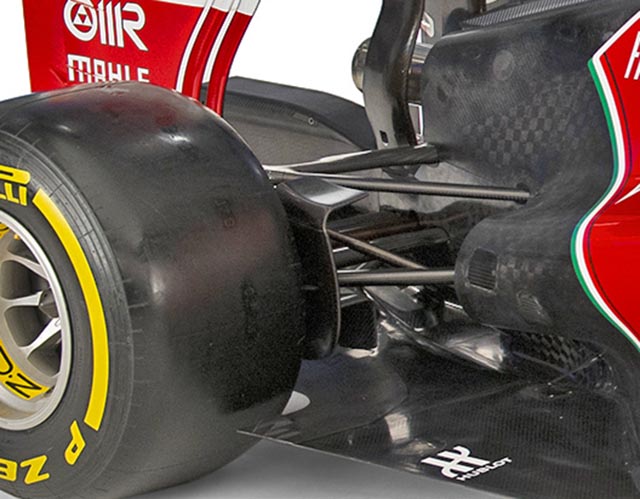
Here we get a really good look at the rear end of the F14-T note the complexity of the rear wing endplates, the small exhaust support on top of the rear crash structure. The diffuser design is also clear, not the strakes with a curved corner at the leading edge.

At Jerez Ferrari conducted a great deal of aerodynamic evaluation runs using all of the usual techniques such as flow vis dye applied to the whole front end of the car (above)

A large sensor array was fitted to the car to study the air flow in the wake of the front wheels (above), a section of it seen is also looking at the airflow in the side pod undercut (below).
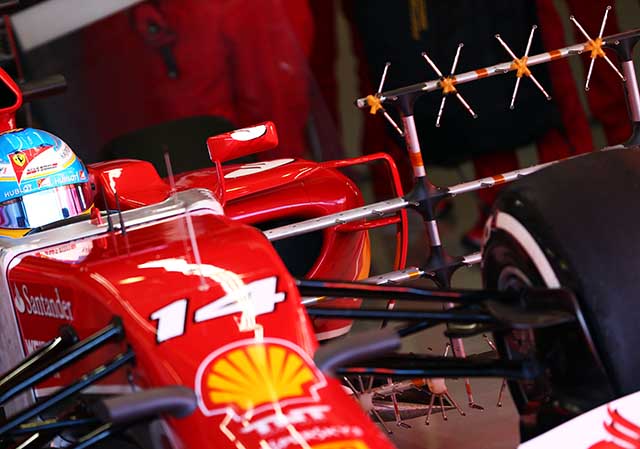

The analysis work covered off various areas of the car like the front brake duct and camera ‘horn’ seen below, clearly showing that these horns do give an aero gain of some sort.

During the test the Ferrari sprouted a couple of additional cooling ducts, one at the base of the sidepod (below) is seemingly similar in concept to the one fitted hastily to the Red Bull RB10.

Meanwhile another (below) appeared on the rear section of the cars upper deck. Both appear to have a cooling purpose.
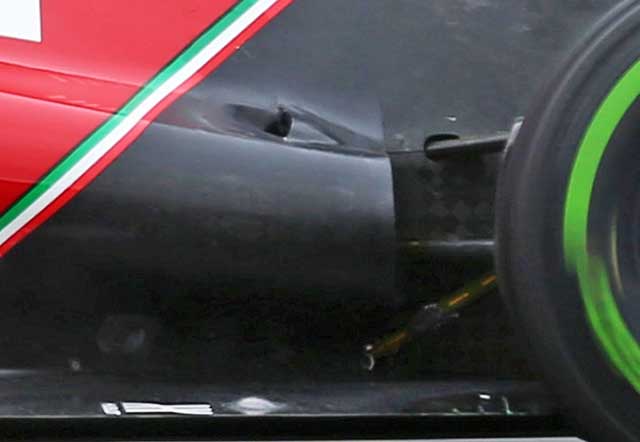

It maybe that the purpose of these two ducts is actually the same as it seems that the car ran with on or other but never both (and on some runs neither!). Here we see the car with the upper duct fitted and the lower one blanked off. Note the flow vis on the rear floor.

TEST 02: SAKHIR, BAHRAIN

At Bahrain the Ferrari appeared with another pitot tube array attached this time at the rear of the side pod. But the engine appeared to expire after a lap, however it did not stop the car running for long.

Ferrari’s engineers have been studying the impact of the hot exhaust gasseson the rear crash structure. Note the temperature strips along its flank. These stickers are used liberally by F1 team and indicate the highest temperature they experience.

A lot of investigation was made into airflow around the wings on the F14-T, here a sensor array is mounted behind the front wing. The location of this could be a hint that the Ferrari wing is an inwash design.
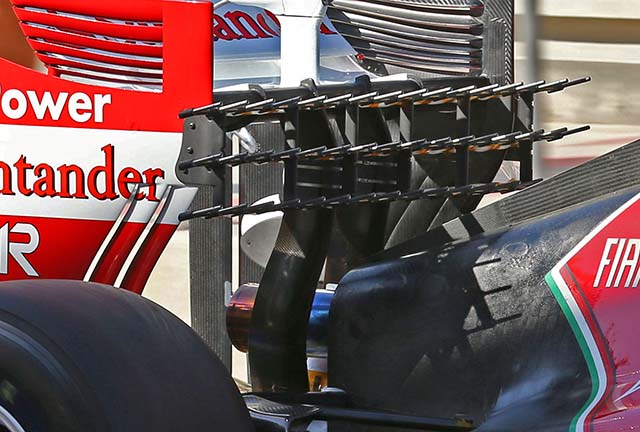

A sensor array was mounted ahead of the rear wing, looking at the flows before the foils. A relatively unusual location for one of these arrays.
TEST 03: SAKHIR, BAHRAIN
Ferrari brought a significant update kit to the final test, and much of the running there was spent evaluating it. With significant changes to the rear end the flow vis paint was evident on the rear wing often.

A sensor array was mounted behind the diffuser which can clearly be seen has a triple deck arrangement, it has featured this since the roll out at Jerez but can be seen very clearly here. The design of the diffuser has changed significantly however, especially in the central section. A bulge – possibly part of the gearbox installation has been smoothed out and the winglet underneath the rear crash structure is not a totally different shape. Note how the lower wishbone shrouds, but does not enclose, the driveshaft.
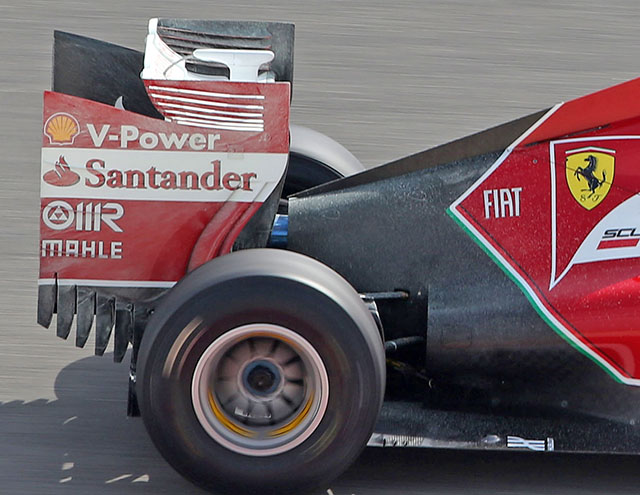

Ferrari uses two types of flow vis paint, the white seen above as well as the more commonplace green. The reason for the two dyes is likely simply the colour of the car, the white dye would be little use on the main section of the rear wing so green is used (below). The rear floor is also coated.

Looking from the rear we get an indication of the flow pattern over the rear wing endplate and the upper surface of the diffuser.
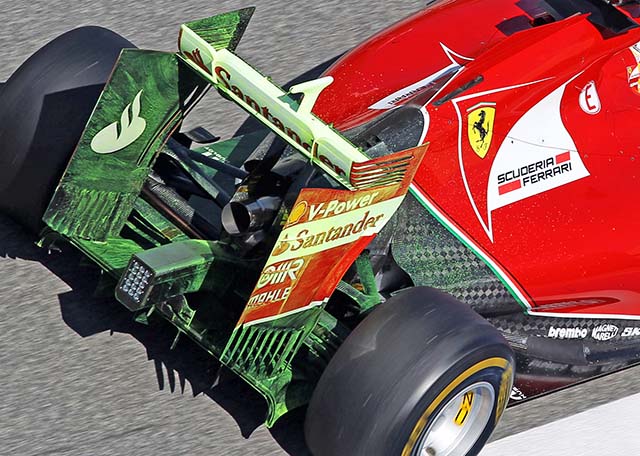

A new front wing appeared at the final test, with a rather more intricate design.

The new wing (above) has three main upper elements whilst the launch spec wing (below) has two. The new endplate is far more simple with just a single opening, the old version having three. Small winglets hanging off the inner face of the endplate are present on both versions (with Shell logos) but the new version is again far more complex. Interestingly the chord of the front wing looks like it may be different on the two versions, as can be seen looking at the leading edges.

The changes were not restricted to the front end, a substantial change was trialled at the rear of the car.

A much larger cooling exit was fitted compared with the launch spec (below), above the exhaust a set of louvres also appeared. This is likely the high temperature bodywork, most likely to seen at tracks like Sepang, and may not be run at Melbourne.
A minor looking but potentially important change could be a pair of flow conditioners on the roll hoop. Note the KERS safety lights.
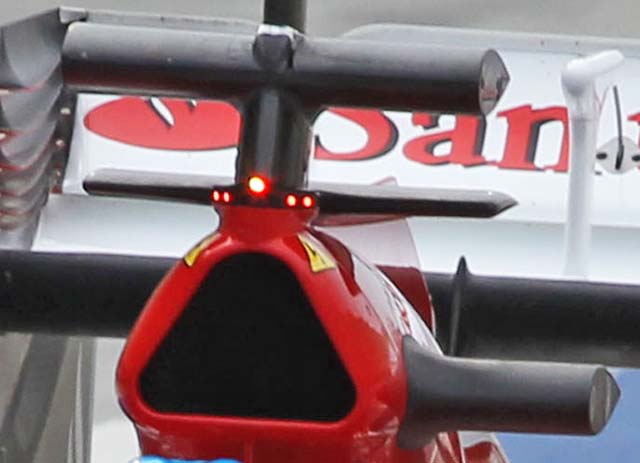

A final sensor array was used to check the airflow around the car with all of the updates fitted (below)

RACE 01: ALBERT PARK, MELBOURNE, AUSTRALIA
Car 07:
Chassis: –
Result: 7th
Car 14:
Chassis: –
Result: 5th (on track) 4th (official).
Before the race Ferrari changed the following parts of the cars
Car 7: Roll hoop carbon cover, Air horn, RHS front brake duct, Nose/front wing assembly, LHS and RHS exhaust manifolds, MGUH controller overcurrent counter
Car 14: LHS and RHS exhaust manifolds, Screw on engine loom, MGUH controller overcurrent counter
Arriving in Australia Ferrari announced that it had extended its technical partnership with SKF, the Swedish bearing supplier has worked with the Scuderia for many years and currently is responsible for the supply of bearings for wheels suspension, transmission, engine and Energy Recovery System, as well as sealing solutions and engineering services particularly in the field of condition monitoring systems. SKF claims it supplies Ferrari with around 150 components, which means virtually all of the bearings assembled on an F1 car.
The first official document recognising the partnership between Scuderia Ferrari and SKF, is a telegram dated back to 1948 from Ferrari congratulating SKF for their technical cooperation which helped Ferrari win the Mille Miglia.
Pat Fry: “Going into this race, getting both cars to the finish seemed like the most difficult task, but in the end, we managed it. Today we saw how reliability can never be taken for granted: it caught some people out and it also affected our performance at some stages of the race. On both the F14 Ts, we had some electrical problems, especially on Kimi’s car, which meant he couldn’t use all the car’s potential. Fernando found himself behind Hulkenberg for many laps and he was only able to show what the car was capable of once he got ahead thanks to a spot on pit stop strategy. Kimi got a great start, but then for much of the race he suffered with graining on the front tyres and thus found himself having to defend, without being able to attack. There is much work ahead if we are to improve the car’s performance. We are up against several very strong opponents, but we have all the right tools to get the job done of closing the gap between us.”
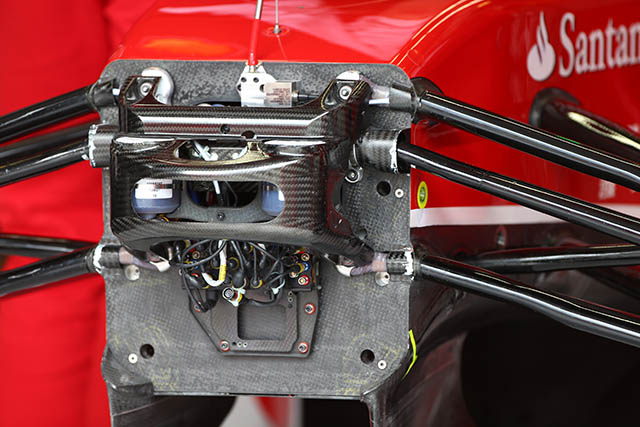
The bulkhead of the F14-T seems uncluttered, but as is common with a lot of the major parts obscured by the carbon fibre cover. One key point of interest is the lack of torsion bars.
RACE 02: SEPANG, MALAYSIA
Car 07:
Chassis: -
Result: 12th
Car 14:
Chassis: –
Result: 4th
Before the race Ferrari changed the following parts of both cars, spark plugs and exhaust manifold.
Additionally the following parts were changed
Car 14: LHS front lower wishbone LHS front top wishbone, LHS coils line, Power steering rack
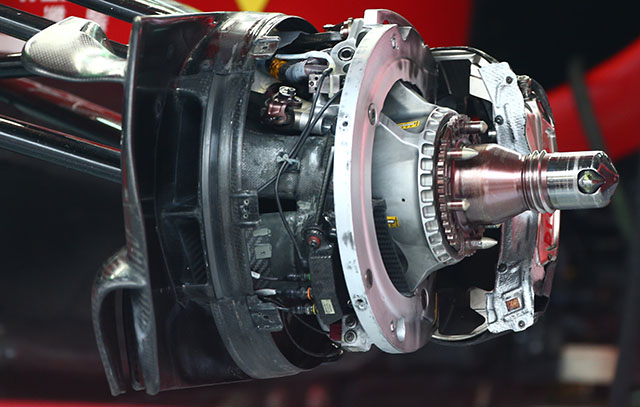
The front brake setup of the Ferrari with the disc and pads removed shows its generally conventional design. As with every recent Ferrari the caliper is from Brembo. Some of the brake cooling elements are just visible.
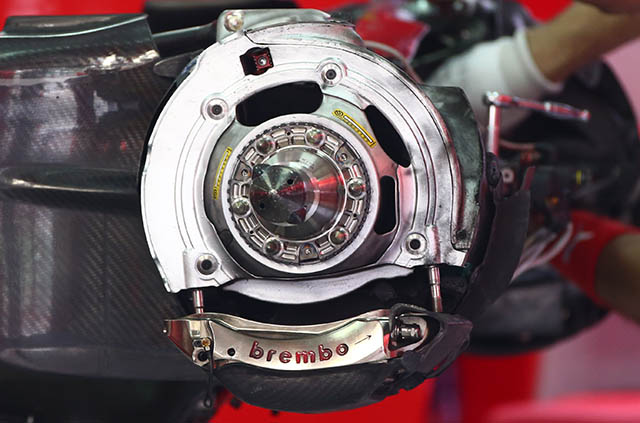

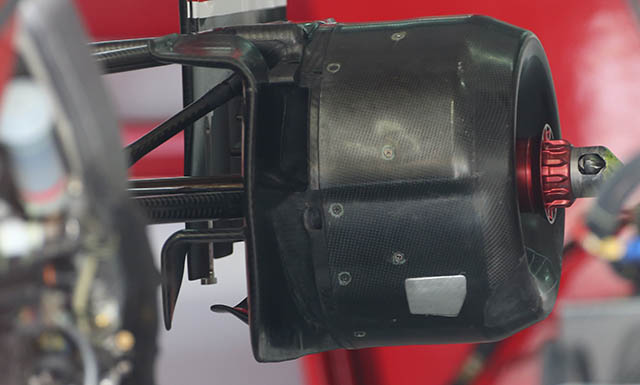
The rear brakes, seen here again with the disc removed mount the caliper at the base of the disc, when the car is running the caliper and disc are fully enclosed in a cooling drum (below).
To deal with the very hot temperatures in Malaysia the F14-T was running lots of additional cooling (below), including a set of gills on the car centreline. It has run some cooling in this location before but not this much.

The car ran different cooling gills on either side of the cockpit, with a shorter more angular set on the right of the car whilst on the left the openings were longer and more curved. This is because the cars have quite different cooling demands side to side.

On the top of the chassis two very small NACA ducts have appeared, these are almost certainly for driver cooling.

Under the side pod duct of the F14-T there is a very cluttered area of electronic boxes, these differ on each side of the car.
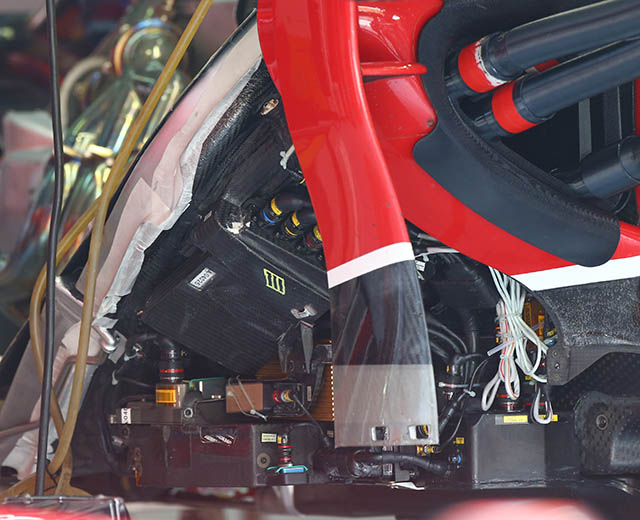
Compare with the layout on the opposing side of the car

RACE 03: SAKHIR, BAHRAIN
Car 07:
Chassis: -
Result: 10th
Car 14:
Chassis: –
Result: 9th
Before the race Ferrari changed the following parts of both cars, spark plugs and exhaust manifold. Additionally the following parts were changed
Car 14: Turbocharger, MGUH
Pat Fry: “Today, we could not have asked more of our car and drivers, because here, our most limiting factor was a lack of top speed. That meant we had to run a defensive race and even if in the middle sector, the one with the most corners, the F14 T was competitive, it was not enough to allow Fernando and Kimi to attack our rivals. In Maranello, we are working on solutions to ensure better power delivery and better driveability. We are also trying to improve the efficiency of the car on the aerodynamic front. The data we acquired in today’s race will provide a baseline for the major checking programme we have planned for the test, right here at Sakhir on Tuesday and Wednesday.”

A look at the rear crash structure on the Ferrari, the rear jacking point is clearly visible. These structures are mandatory on all cars but the teams have freedom of design.
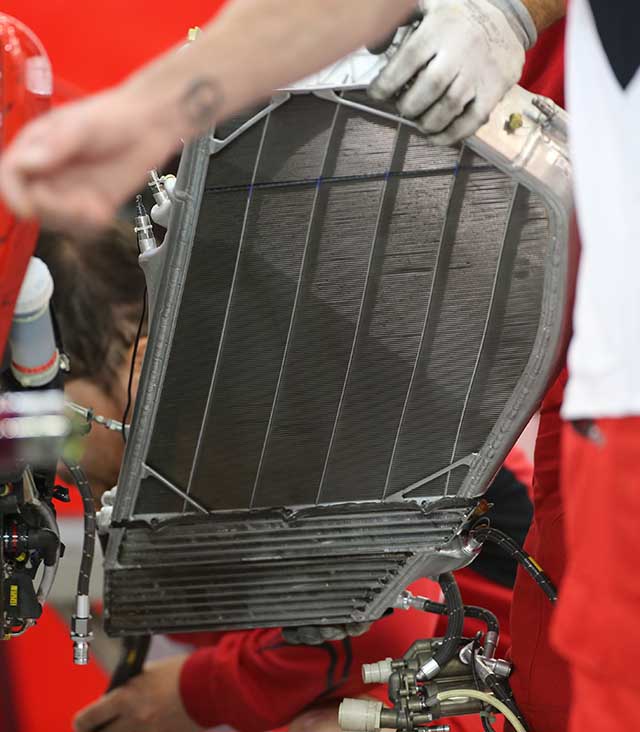

The main cooler in the left hand side pod removed from the car. It is split in three with some of the KERs cooling in the lower parts. When installed on the car the cooler is canted forward (below)
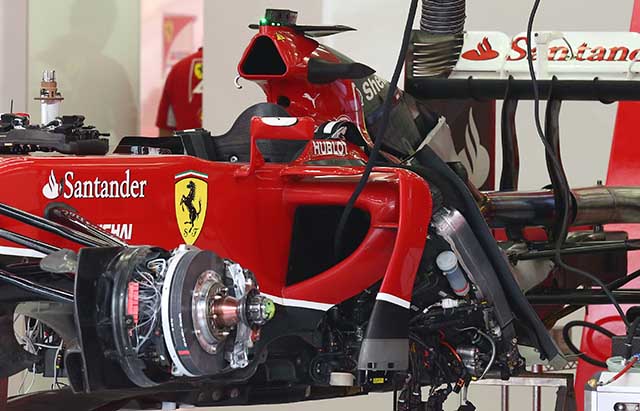

With the carbon fibre cage removed a little more detail can be seen on the Ferrari bulkhead, the master cylinders suspension pickups and wheel tethers are all clear to see as is the electronic box. also just visible is the steering rack behind the bulkhead. Note – no torsion bars are evident.
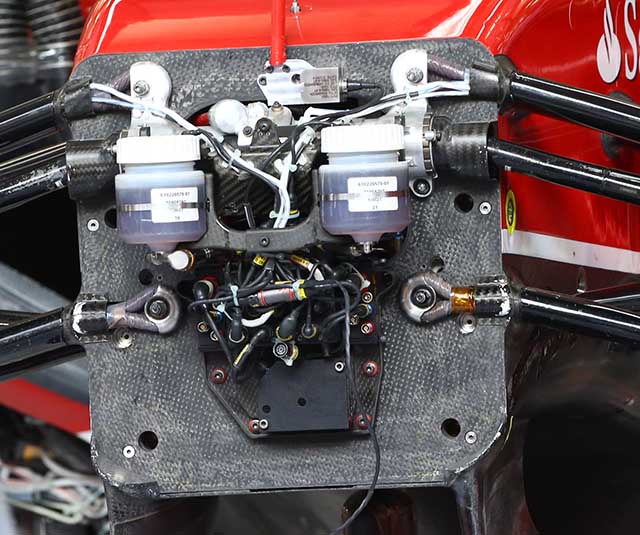
Underneath the nose horns on the Ferrari there is a metal camera mount. By regulations all cars must run two front camera positions Ferrari is using its cameras for a small aero gain.

RACE 04: SHANGHAI, CHINA
Car 07:
Chassis: -
Result: 8th
Car 14:
Chassis: –
Result: 3rd
Before the race Ferrari changed the spark plugs on both cars,
Additionally the following parts were changed
Car 07: RHS front brake duct internal panel, LHS rear view mirror

Ferrari’s composite gearbox is shared with Sauber and Marussia, here it can be seen without any extra parts attached. The suspension pickup points are all clear to see.
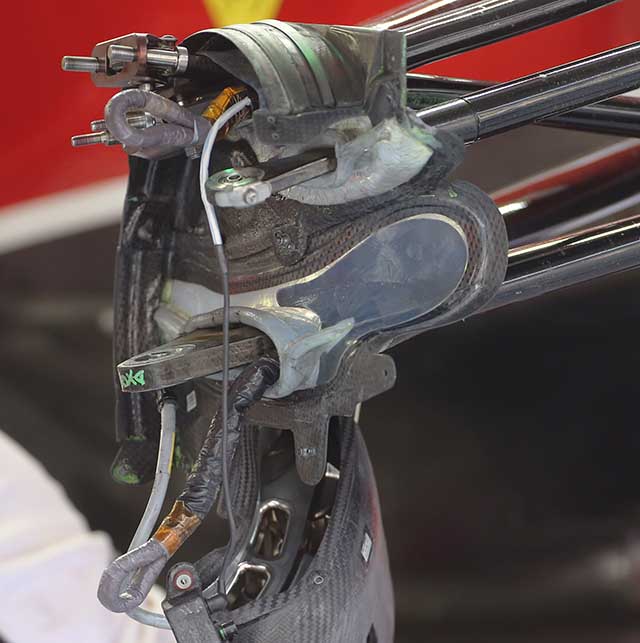

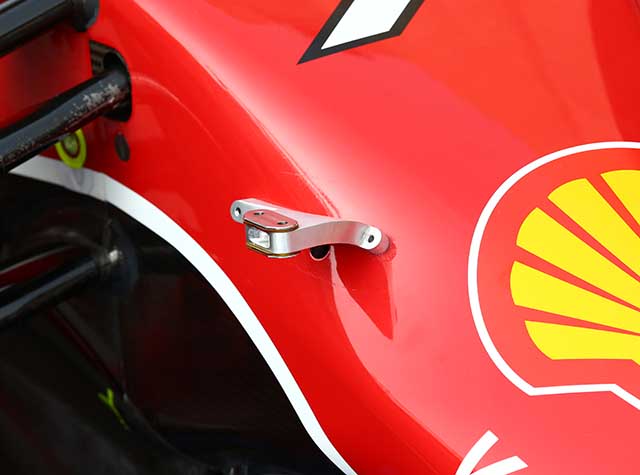
In Shanghai the team fitted a new upright design to its cars. With the upright removed the outer part of the suspension arms can be seen with rod ends embedded in composite parts.
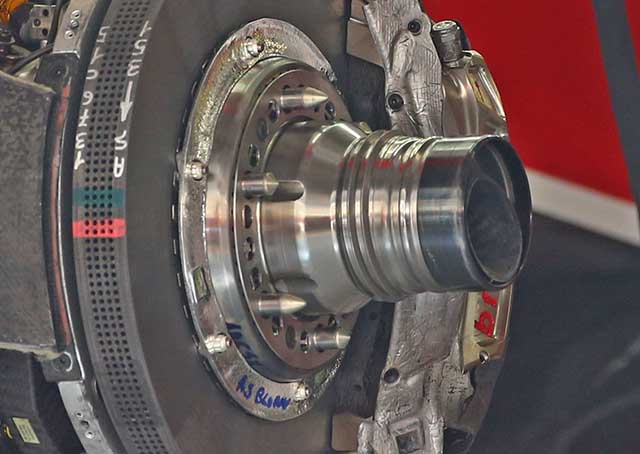

The reason that the uprights were removed was to allow a new design to be fitted. It features the ‘blown hub’ concept seen on a number of cars last year. This aids the flow around the wheel and is said to reduce drag.
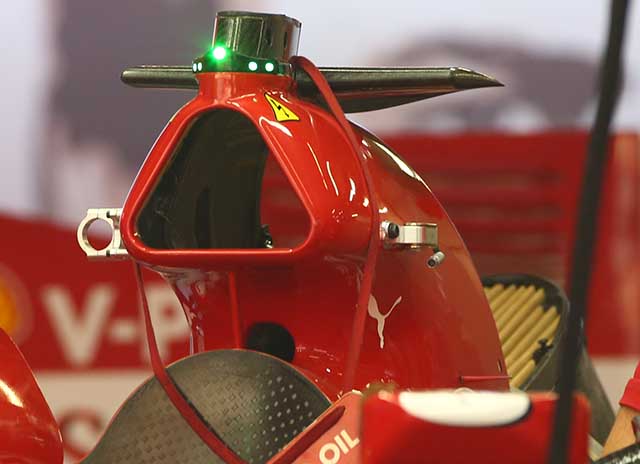

With the rear end removed the roll hoop is clear to see, the medal lugs on either side are camera mountings. The air filter is just visible.
RACE 05: MONTMELO, SPAIN
Car 07:
Chassis: -
Result: 7th
Car 14:
Chassis: –
Result: 6th
Before the race Ferrari changed the RHS inginition coils of both cars,
Additionally the following parts were changed
Car 14: Rear brake calipers, Rear brake friction material, Adjust model of MGUK DC power (at FiA request)
Car 7: Hydraulic QD’s between MOOG block and radiator
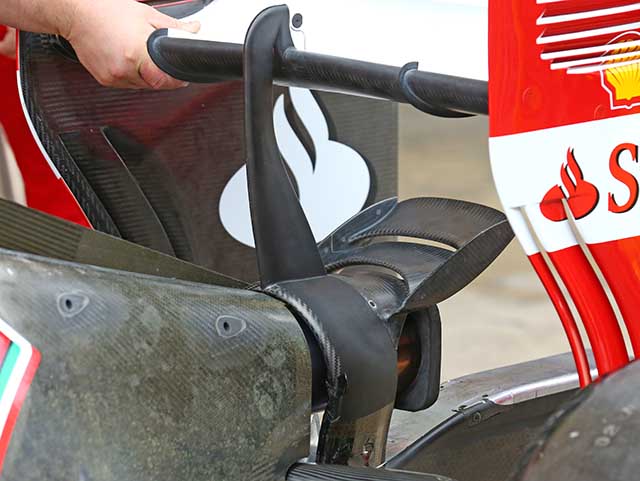

Ferrari arrived in Spain with a different rear wing concept. The new version apes Marussia in that it uses a single central support with a Y-lon split above the tail pipe. A monkey seat winglet has also been added.
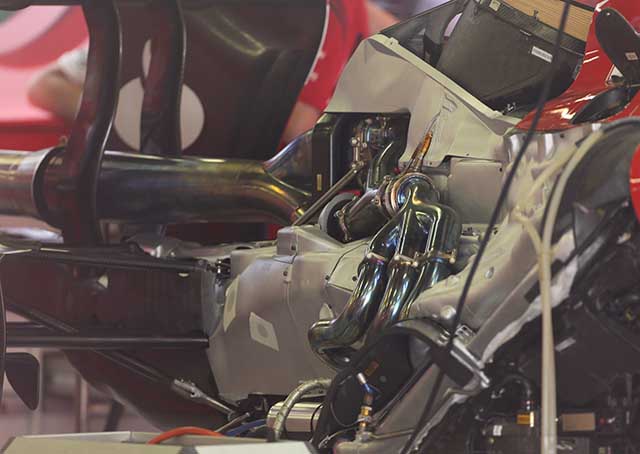

A good look at the rear of the Ferrari with the heat shielding added to the car, it is notable that the layout is much more angular than that of the Mercedes. The exhaust layout is of interest, seen more clearly below. The headers curve around the cylinder head and then join together in a collector (one on each side linking three pipes) downstream of the collectors the pipes then split in two.
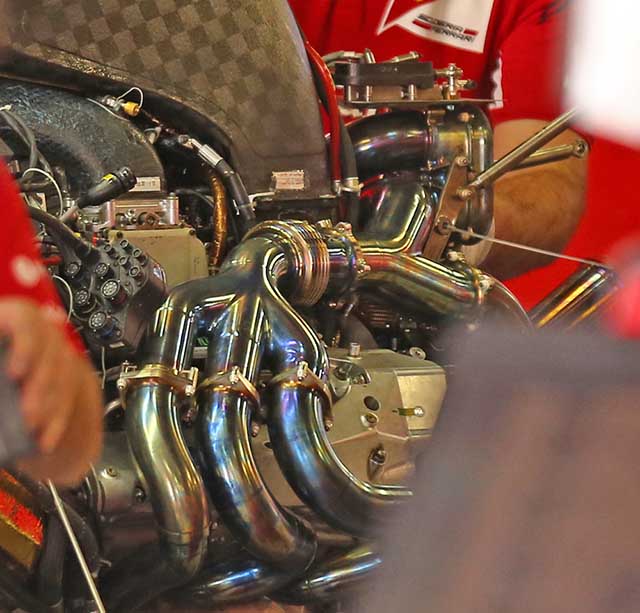

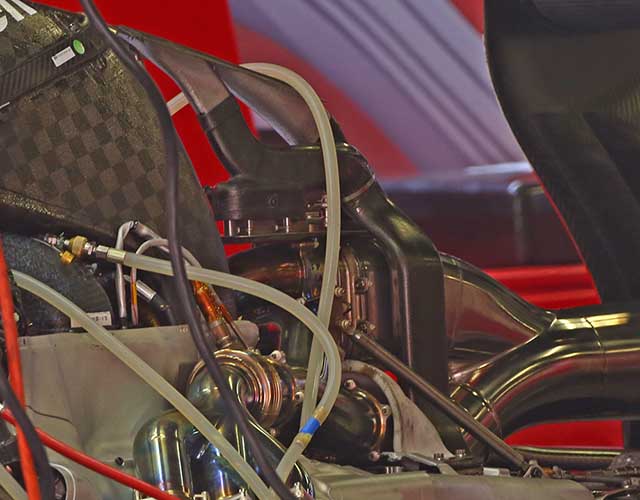
The Ferrari turbocharger has yet to be seen anywhere but it is thought to be mounted in the bell housing area. It reportedly is split in a similar (though less extreme) way that the Mercedes design is with a MGU-H sat between the two sides of the turbo. The pipes heading down to the turbo can be seen on the image below. The other pipe heads upwards to a unit thought to be the wastegate. The left bank of enters the housing at its base whilst the right bank enters it above. A single exit pipe joins with the pipe leaving the turbo charger.

Ferrari conducted some flow vis running in Barcelona to evaluate some aerodynamic updates on the car.















