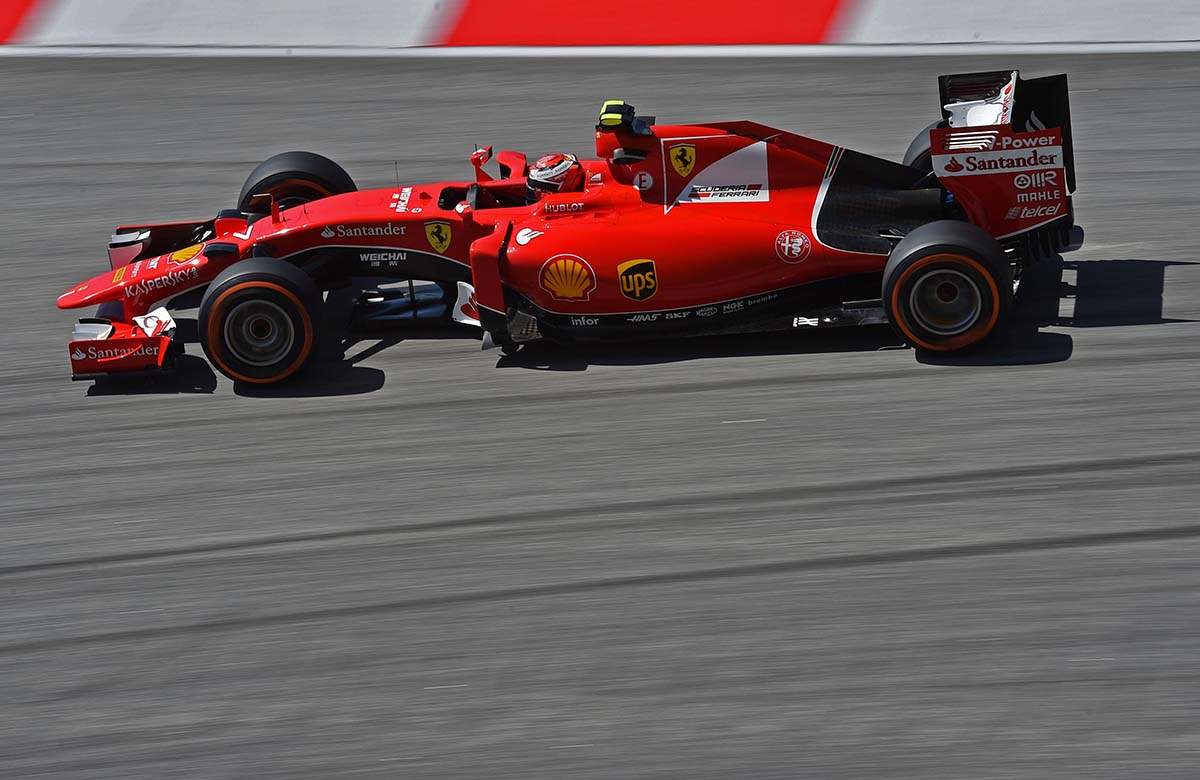
The SF15-T the sixty first car built by Ferrari specifically to take part in the Formula 1 World Championship. It is the second car made by Ferrari since the reintroduction of turbo engines in 2014. In 2014 the Italian marque struggled badly with a power unit that was overweight and under powered.
Chassis
The most striking visual difference between the SF15-T and its predecessor is the lowering of the front end of the car in accordance with the change of regulations for the 2015 season. After a few seasons of rather unappealing aesthetics, the 2015 rules permit the SF15-T an attractive nose shape which also brings excellent aerodynamic performance according to Ferrari. The long nose is at odds with many teams who are trying hard to shorten their noses.
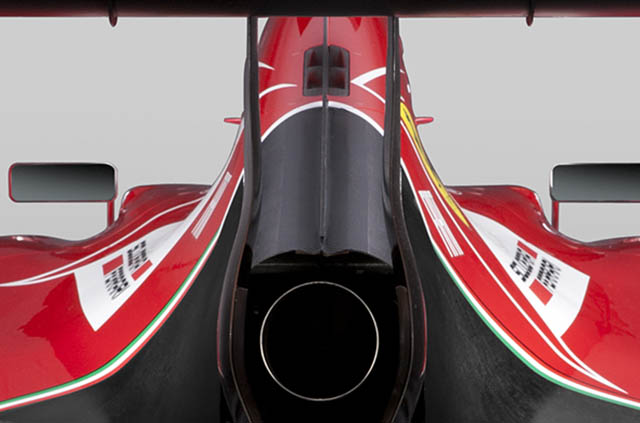
A casual glance at the back of the car reveals a much more tightly packaged rear end which allows more downforce to be extracted from the critical surfaces around the rear of the car. The rear wing family has been extensively redesigned to deliver stable performance in corners while producing a larger DRS effect on the straights.
The front and rear brake ducts have been remodeled to produce more cooling of caliper and brake disk while generating more downforce than their 2014 counterparts. Both front and rear suspension kinematics have been overhauled to present the tyre to the road in a manner that allows better use of the Pirelli rubber.
As in 2014, the current rules place heavy emphasis on the strong integration of Power Unit and Chassis. Integration is not just about packaging – finding neat homes for all the myriad equipment in the car – it is more about making sure that the PU and Chassis are specified so that the resulting vehicle will have the highest possible performance. A range of carefully chosen design targets ensure that the SF15-T has optimum choice of cooling to provide the best overall downforce and power levels. In addition to carefully designed internal airflow, the SF15-T has a much improved cooler matrix layout that allows several tenths of a second per lap compared to the previous year.
Analysis
Overall the SF15-T is a continuation of the concept seen on the F14-T, though Ferrari will hope that many of that cars short comings have been resolved. One issue the Ferrari power unit had in 2014 was that it was over weight and did not produce enough power. But the minimum weight increase of 11kg over 2014 will certainly help in that department.

The SF14-T features twin cooling slots on the centre line of the engine cover (above). These are similar to those used on the F14-T (below). This centre section of the rear bodywork is one of only a few places where teams can place additional cooling ducts. Most of the rest of the bodywork must be continuous with no holes.
The purpose of the slots on the engine cover is almost certainly the same as it was in 2014, cooling the turbocharger, as can be seen on this picture of the F14-T showing the cooling pipes from the duct feeding around the very large waste gate on the Ferrari V6.
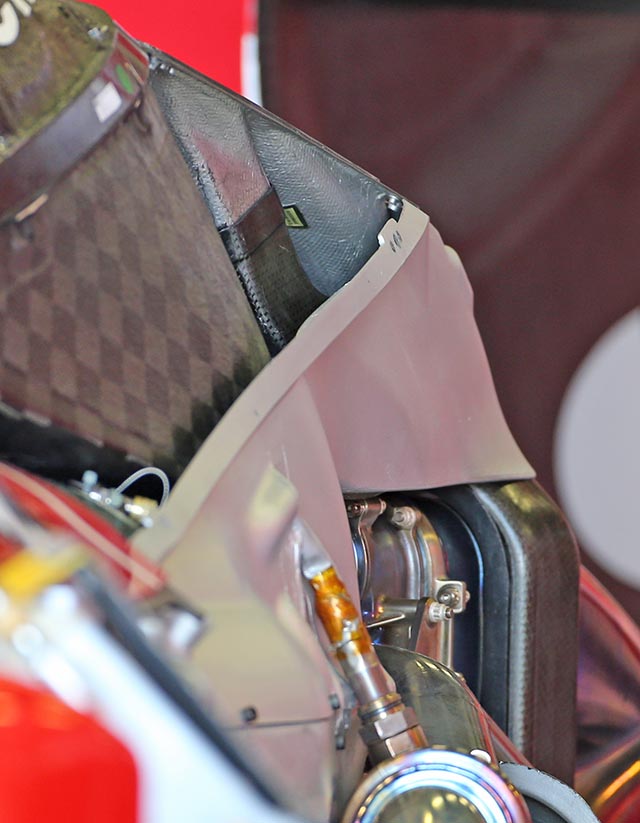

With the slots seemingly the same size as the 2014 versions and in it suggests that perhaps Ferrari has not opted to split its compressor and turbine any more than it had done in 2014, where they were split but both mounted at the rear of the V6. It should be noted though that the ducts now sit notably further forward on the engine cover. It could be that Ferrari is developing its own Mercedes style totally split turbo to introduce later in the season.

The cooling package on the SF15-T also seems to be very similar to that of the F14-T, though perhaps the sidepod ducts are slightly smaller. The overall shape and concept of the ducts though is very similar when you compare the 2015 design (above) with the 2014 design below. The new car appears to have a slightly larger undercut at the leading edge of the sidepod.
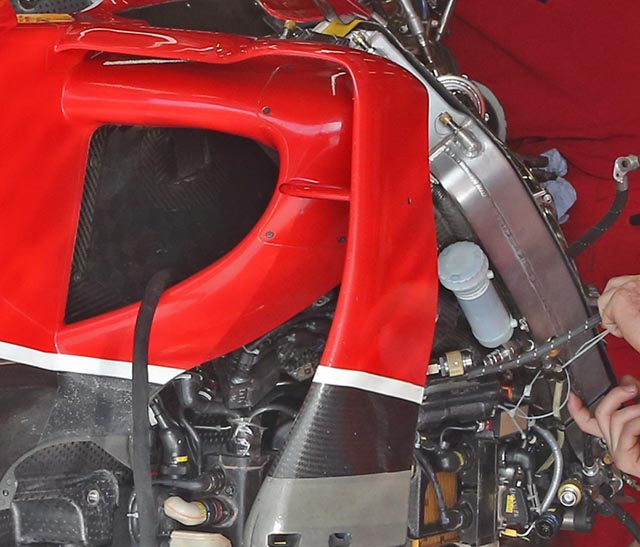

This reduction in size is to be expected as according to the Ferrari PR material (posted above) the SF15-T has an ‘improved cooler matrix layout’. Optimising the heat exchanger position and detail design can indeed bring big gains but it is a specialist task which Ferrari has probably outsourced.

From the rear however there seems to be little difference between the under cut at the front of the side pod on the new car (above) and the old (below)

The roll hoop and associated air ducts on the SF15-T (below) appear similar in concept to the 2014 design but there are a number of subtle differences. The overall shape and size of the main duct, which supplies combustion air to the V6 engine seems to be unchanged.
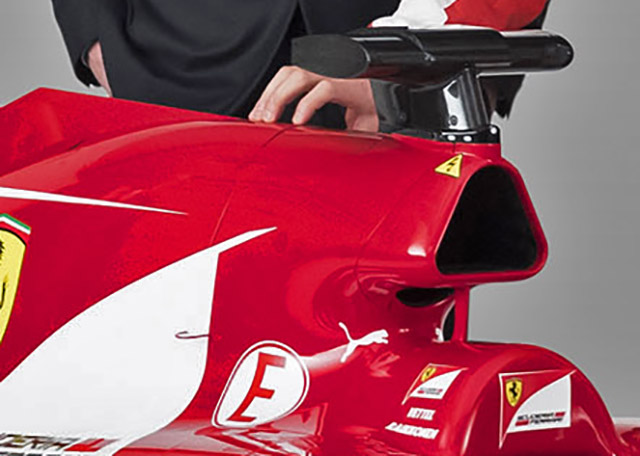

The roll hoop support which leant forward slightly on the old car has been replaced with a straighter but thicker design on the newer car. Compare the 2015 design (above) with the 2014 version (below)
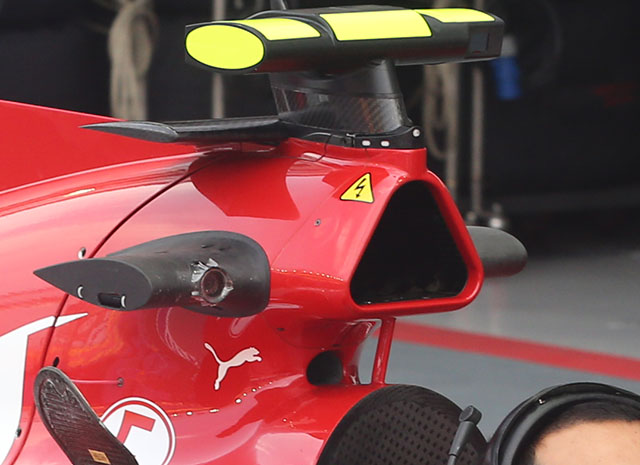

The cooling duct beneath the main duct (thought to be for electronic boxes) has moved upwards and grown significantly in size. One of the more interesting differences between the two cars in this region can be seen in the comparison pictures above, the distance between the front of the roll hoop duct and the downward sweep of the engine cover.

This can be seen easily when comparing side on views of the two cars (SF15-T above and F14-T below).

On the new car there is a much longer distance between the front of the roll hoop inlet and the rear of the monocoque (which can be seen when looking at the panel join lines), additionally the flat topped section continues even further back than before. The reason for the extension is not yet clear but will relate to air flow to the power unit. It may be that if Ferrari has adopted variable inlet trumpets as allowed under the 2015 rules then the increased height this will cause in the plenum and associated ducting may cause the difference.
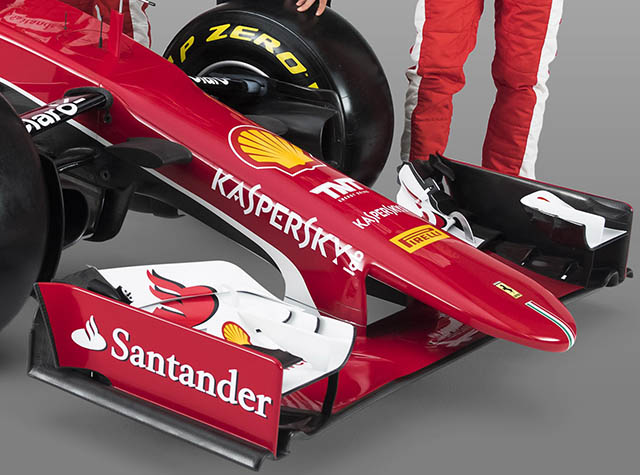

There will inevitably be much discussion about the nose and front of the SF15-T but the nose seems to be relatively conventional in concept for a 2015 car on first impressions.
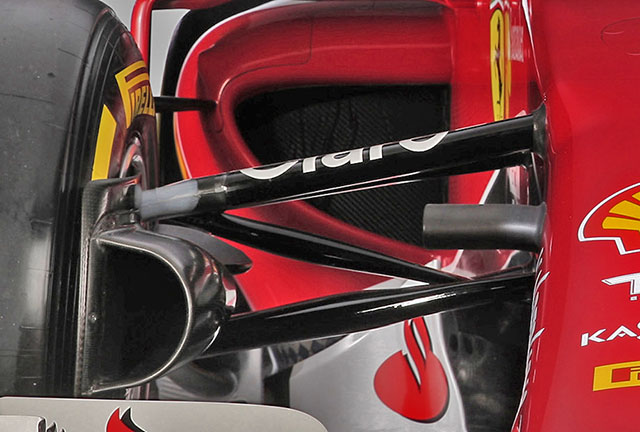

The SF15-T retains the pull rod actuated front suspension used on the 2014 car. Note the TV camera housing position.
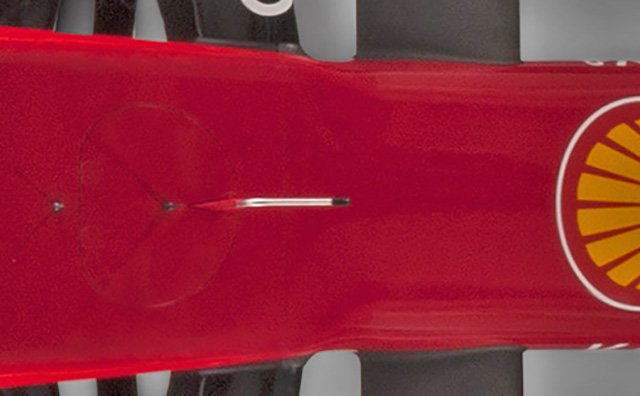
The nose narrows slightly just ahead of the front bulkhead and the forward inboard front suspension pickups.
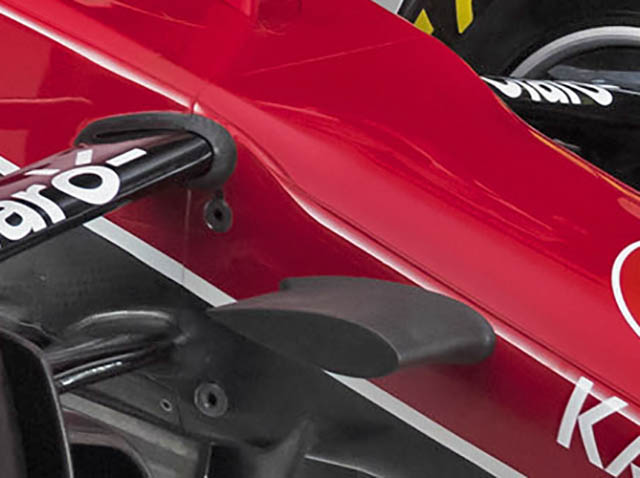

Looking more closely at the panel lines on the front of the car it appears that the Ferrari has a flat bulkhead, as is typical, just forward of that where the nose can be seen to narrow from the top view a small step in the nose is also visible. This layout aims to maximise the space for suspension components which has been reduced by the overall gradient of the nose.
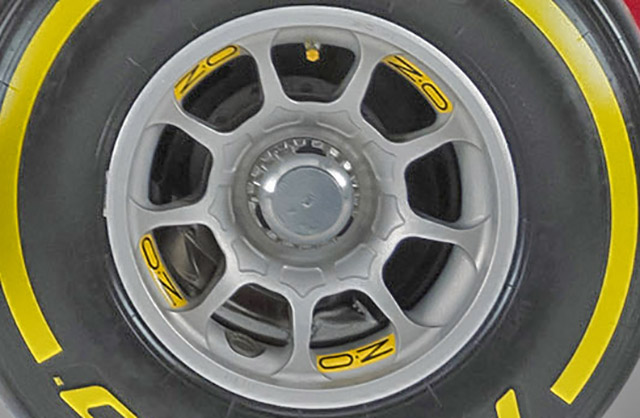

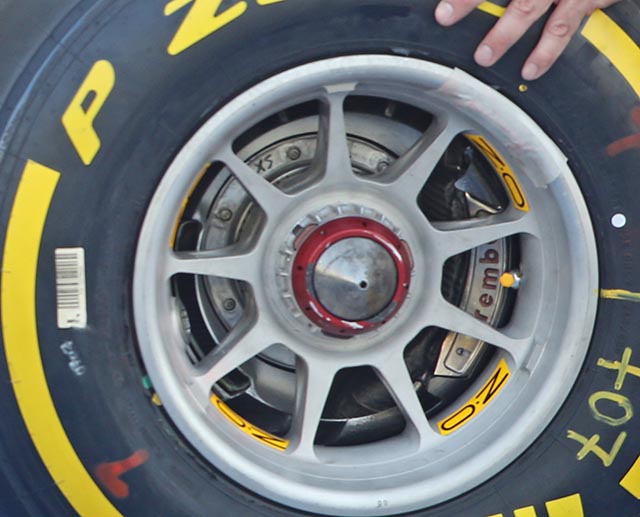
Ferrari has adopted a new design of OZ wheel for the SF15-T. Compare the new front wheel (above) with the old (below). The small piece of tape on the 2014 wheel covers the balance weights normal for all wheels, road or track. On the new car it is also worth noting that the brake calliper has been moved from the trailing edge of the disc to the base, though still slightly rear of centre.

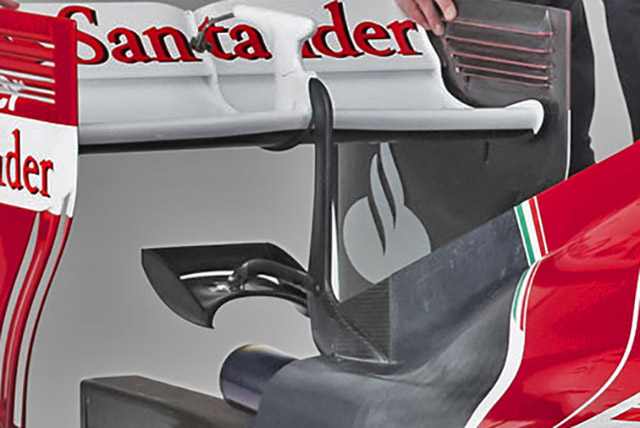
The rear wing support is an evolution of that used on the F14-T with the central pylon connecting to the trailing edge of the engine cover. A more substantial structure likely mounts to the top of the transmission casing.

At the heart of the Ferrari 2015 design is an extensively reworked power unit. In 2014 the team decided to compromise the overall output in favour of making the V6 engine as compact as possible. In theory the aerodynamics department should have been able to capitalise on this to make the overall car faster overall but it did not work out that way.
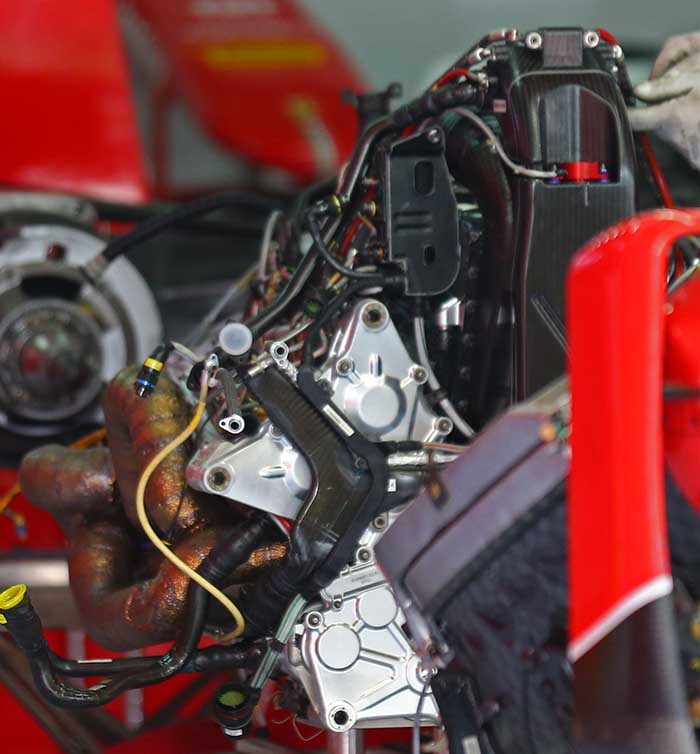

Looking at the 2014 power unit (above – fitted to a Marussia MR03B) and the 2015 version (below) the differences are clear to see.
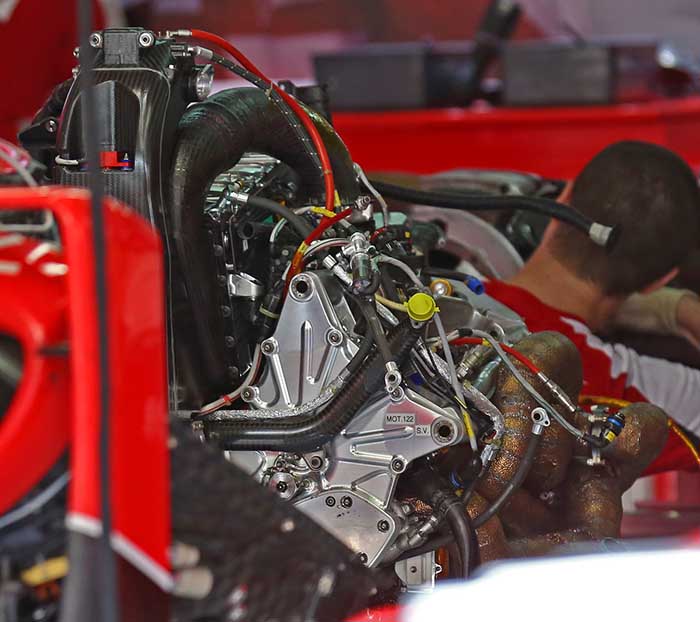
The oil tank on the V6 has been relocated, on the 2014 design it was located in the transmission, but in 2015 it has returned to the conventional location at the front of the V6. The intercooler concept remains the same as in 2014 though has a slightly different shape. The wastegate layout is totally new.
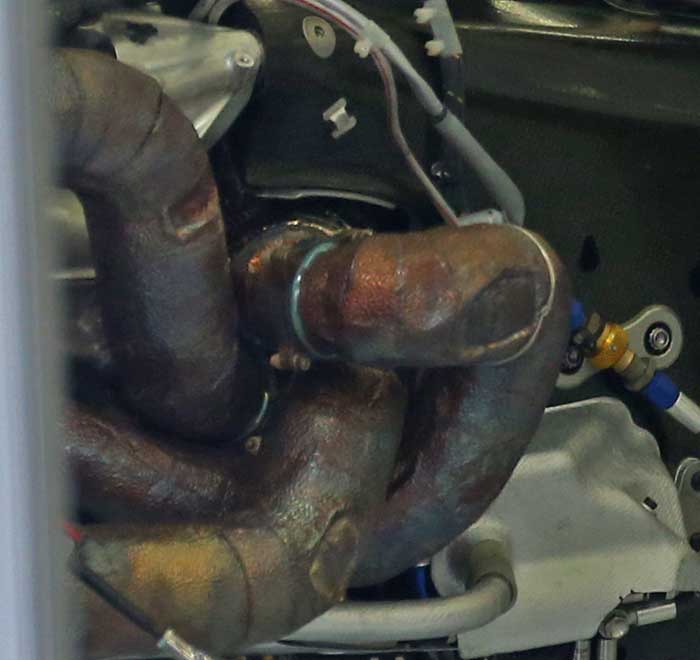

The 2015 V6 engine has a totally different exhaust concept, the up and over approach of 2014, designed to make the ICE more compact has been replaced by a more conventional 3 into 1 manifold. No clear image of the collector is yet available as it sits close inside the bell housing along with the turbocharger.

This layout with the turbo fully enclosed has a big impact on the gearbox design, which features a large hole in its casing so that the exhaust can exit.

Overall the gearbox casing is structurally similar to that of 2014 in as much as both use a carbon fibre case and have pickup points for pull rod rear suspension. Sauber also uses the Ferrari casing.
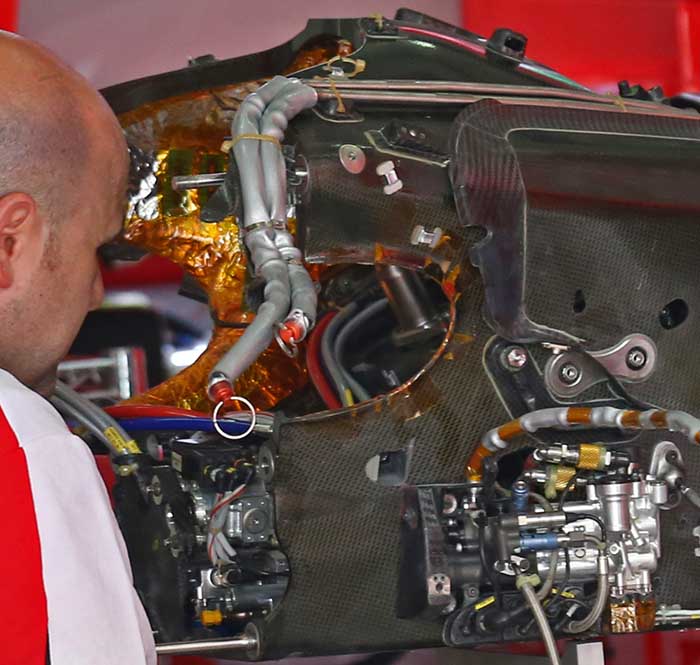

The bell housing of the Ferrari & Sauber is a busy place not only does it host the two exhaust collectors and turbo (something that requires significant heat shielding to be applied to the inner face of the case) it also hosts some major hydraulic components, the rear suspension torsion bars (and one assumes the dampers but these have not been seen yet).

Here we get a look at the rear suspension assembly with torsion bars, which can be removed from the bell housing as a single unit.
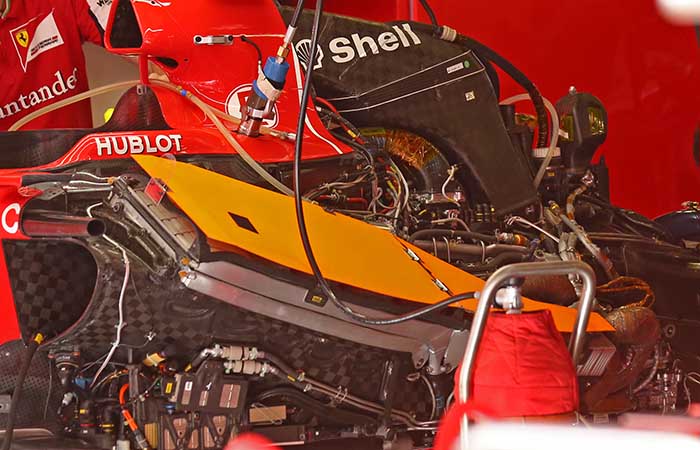

The cooling system of the 2015 Ferrari has been heavily revised, and at the opening races the Italians were keen to keep the design of their heat exchangers under cover. After all the pre season press releases had claimed that the new more efficient cores were worth a few tenths of a second a lap on their own.

While the detail is not yet apparent images of additional slats on the rear of the heat exchanger on the RH side pod have appeared. At first it was thought that these were some sort of shipping device to prevent damage to the radiator but not a theory has come out that suggests that this is part of the new technology the team has alluded to. It could be that the fins cause the airflow through the cores to be more turbulent and allow better heat exchange. It is something that has been experimented with by Japanese company Denso – “This design change allowed the radiator to have 10 percent more efficient heat rejection than DENSO’s conventional radiators”

The cooler layout differs on the left, as does the technology of the coolers themselves as can be seen as one is fitted here.
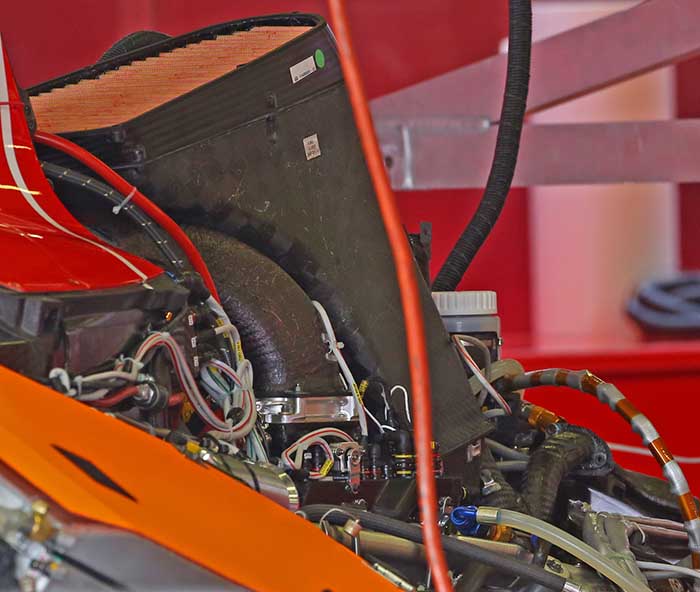

A look at the air filter housing shows up the fact that Ferrari has a somewhat unconventional plenum.
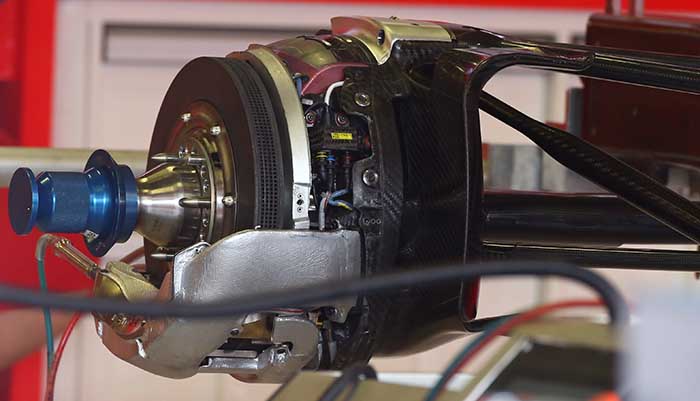

A look at the Ferrari brake setup at the rear with the calliper mounted at the base of the disc for the lowest CofG.
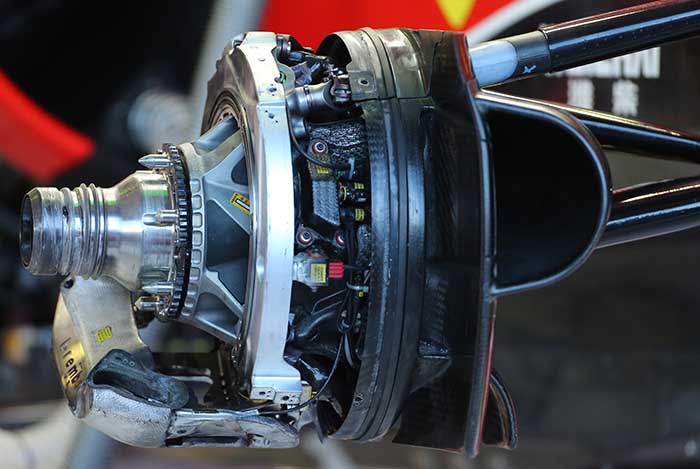

The front brake setup with friction material removed (above) and fully assembled (below), the white section on the outer edge of the upper wishbone is reported to contain some kind of spring based system for ride height control.
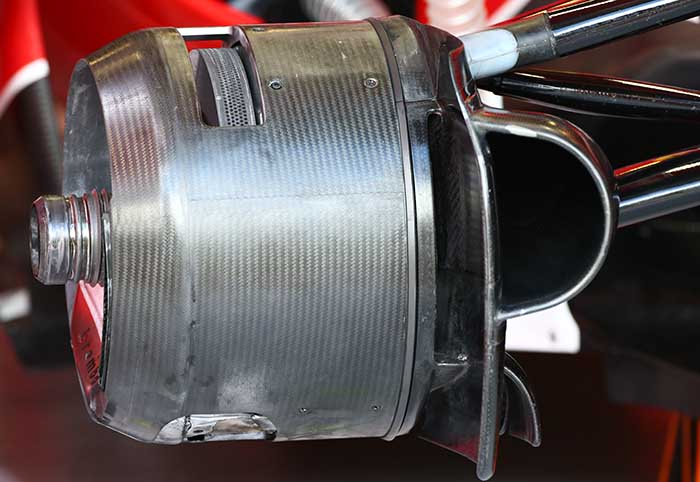

The brakes in component form (below)

The Ferrari features four cooling ducts on the centreline of the engine cover.

The rear wing mounts to the transmission casing via an evolution of the Y-lon support initially pioneered by the Marussia team.
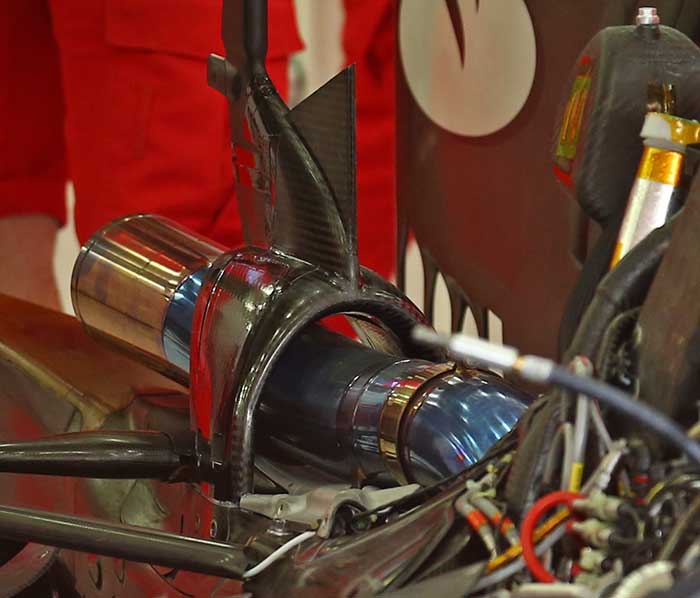 .
.




