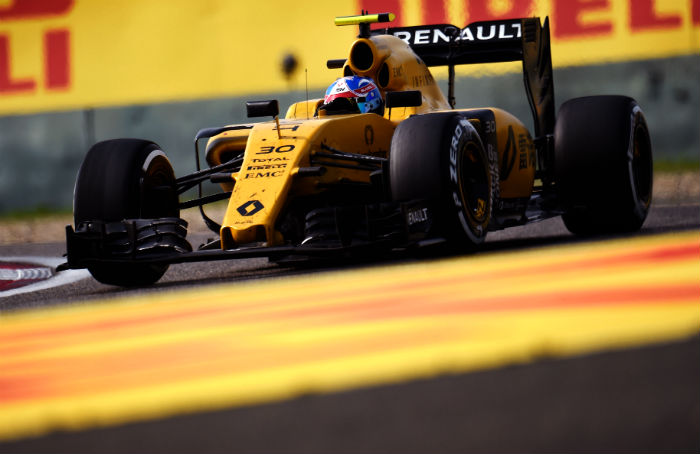
The story of the Renault RS16 is very closely linked to that of the Lotus E23. Indeed Renault’s return to Formula 1 as a full works team was made possible by the financial collapse of the Lotus team in late 2015. However at the official launch of the RS16, and indeed the new team in Paris early in 2016, the wraps were taken off a very gently modified Lotus E23 rather than the final RS16.
Asked to clarify the situation the team admitted shortly after the covers came off that the car in Paris was an E23 based show car but that the RS16 would be a new chassis. But the final RS16 stretched the definition of new to the limit – and it could almost be described as a B spec E23. The reason for this is simple, the struggles of the Lotus team saw many staff leave the operation and development on a proper 2016 design stalled.
“We were advanced with the development of our chassis with the previous power unit (Mercedes) but our focus shifted as the likelihood increased – and was ultimately confirmed – that we would become part of the Renault family once more. It was a very late switch in the development programme for the 2016 car, which has meant a tight schedule with the chassis. It’s been a super compact programme, but we’ve seen with the homologation of the chassis that we can react quickly and do a great job” Nick Chester admitted. “We want to improve reliability, develop the integration between the chassis and the power unit, all with the target of having a far more integrated car for the future.”
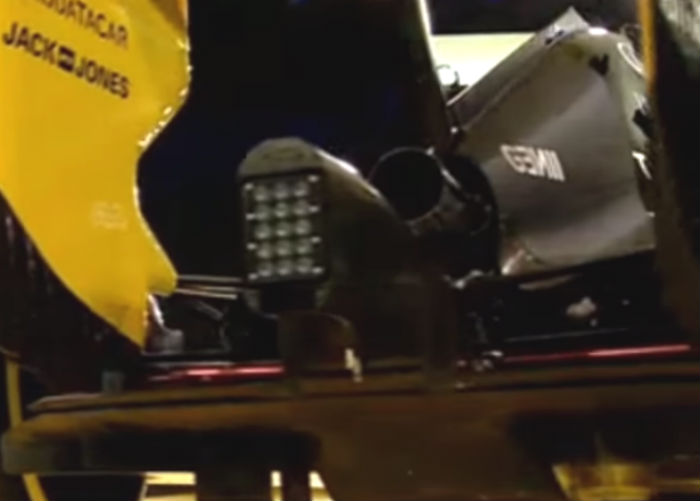

The E23 based show car in Paris did at least have a 2016 exhaust fitted, with the new additional second wastegate exhaust exit visible (above) which complied with the regulations but was far from the final design.
The real Renault RS16 made its debut during a brief roll out in Barcelona and it was imediately clear just how similar the RS16 was to the E23, indeed visually there was very little difference between the two. Partly this is because of the strange gestation of the RS16. It was originally designed by the Lotus team to accommodate a Mercedes V6 power unit, but Renault’s purchase of the team saw it reworked to accommodate the Renault power unit.

The cockpit sides are the most obvious difference between the E23 (below) and the RS16 (above), new rules forcing them to be higher and stronger.

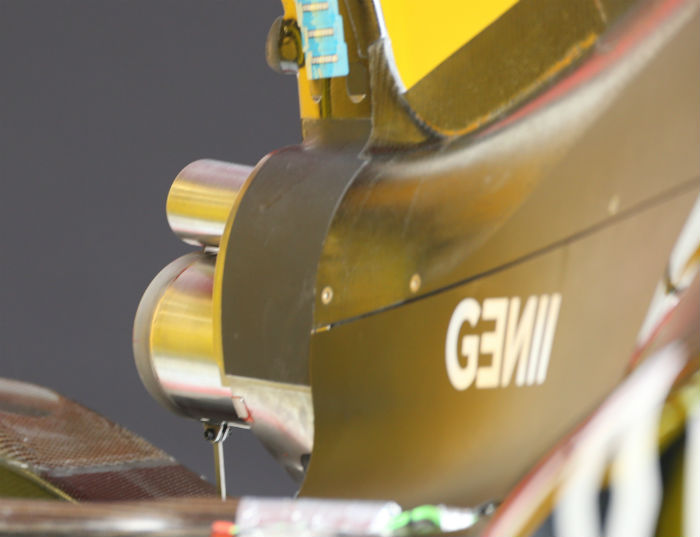
Another difference comes at the rear of the car with Renault opting for a single wastegate pipe rather than the two chosen by most other teams including its customer Red Bull.

The RS16 retains the same transmission as the E23, though in modified form, not least to suit the rear face of the Renault RE16 power unit which is very different in terms of shape to the Mercedes V6.
One of most noticeable features of the E23 & RS16 is the roll hoop duct arrangement. Alongside and slightly below the conventional inlet for combustion air there are two extra ducts, the purpose of these has yet to become fully clear but it is likely that they feed a heat exchanger mounted toward the rear of the power unit. A fourth much smaller duct sits directly behind the drivers helmet.

This layout suggests that substantial amounts of the monocoque design carried over from the E23 to the RS16.
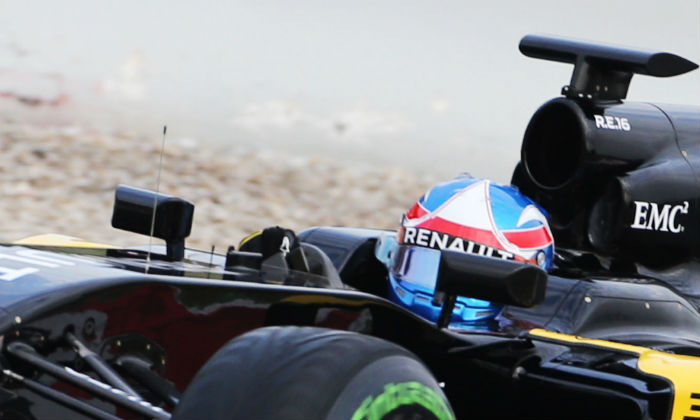

Looking at the overall chassis design of the RS16 (above) you can see just how close it is to the E23 (below) especially at the top of the tub.

Overall the design of the E23 was very close in many areas to that of the E22. This is something that can be clearly seen by looking at the shape of the roll hoop, which appears identical on both cars. The front of the chassis is slightly lower on the E23. Compare the 2015 car (above) with the 2014 (below).

Details of what developments have gone into the power unit over the winter but Remi Taffin has stated that “Like the chassis, the PU we use this year is a continuation of the work we started last year with some concepts taken further. We have made some changes to the combustion chamber, turbo and electronics to give more power, without sacrificing reliability.”
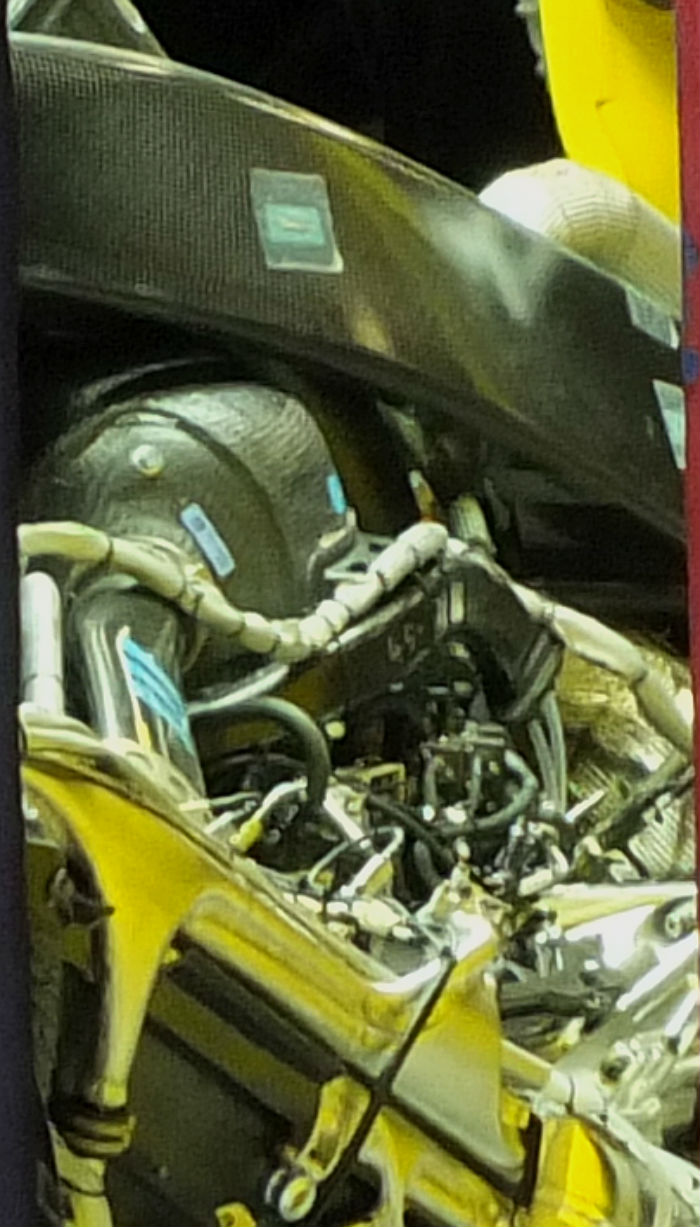

Looking at the 2016 Renault PU (here fitted to the RS16-above) and comparing it to the the 2015 unit (below) it is clear to see that the plenum has been redesigned, this also suggests that work has been carried out on the variable inlet system on the RE16.

The now very yellow Renault sported a new nose in Melbourne. In this image the old Lotus E23 nose which was used in testing can be seen behind the new design in the foreground.

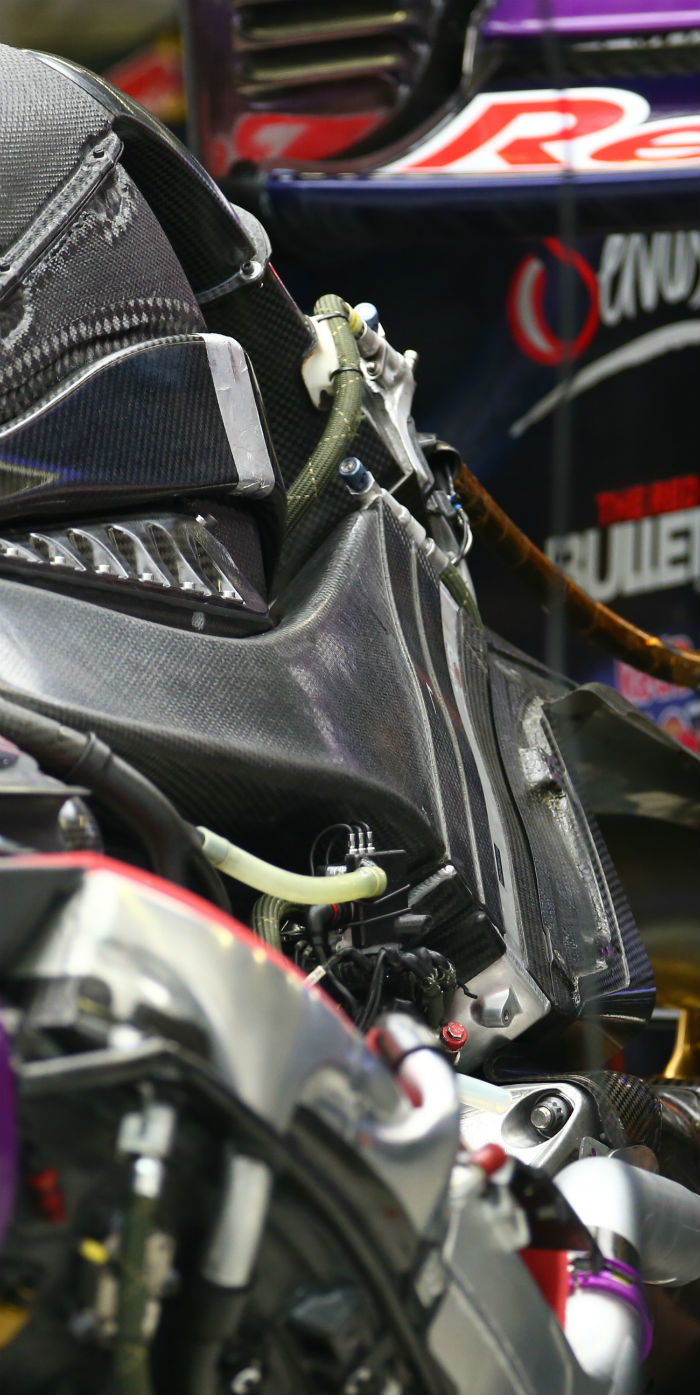
A look at the front bulkhead of the RS16, note the step in the chassis. This design is essentially the same as the E23.
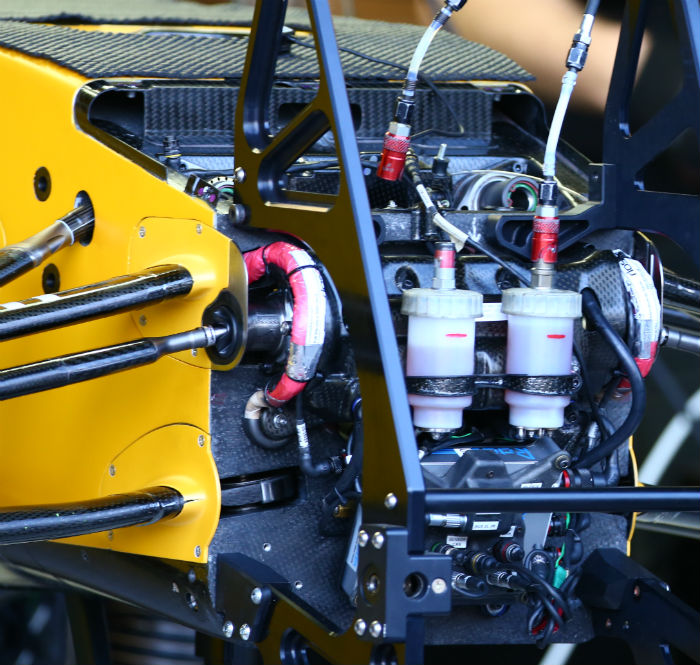
Compare the new Renault RS16 front bulkhead with the Lotus E23 front bulkhead (below)
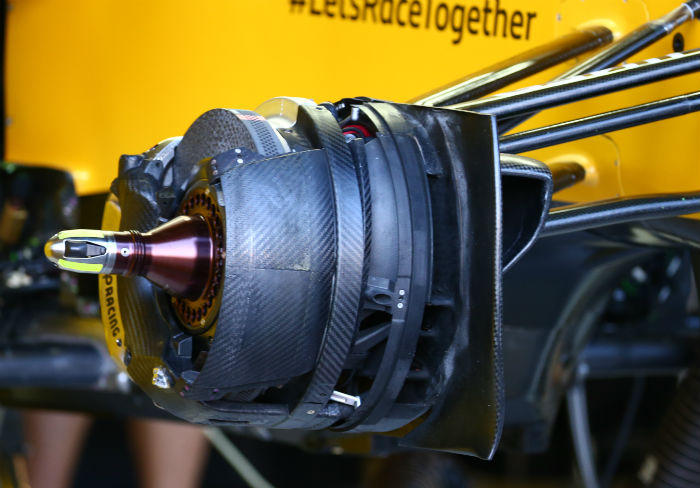
A look at the front brake setup on the RS16, Renault opting for the less common AP Racing calipers (made bespoke for the car)
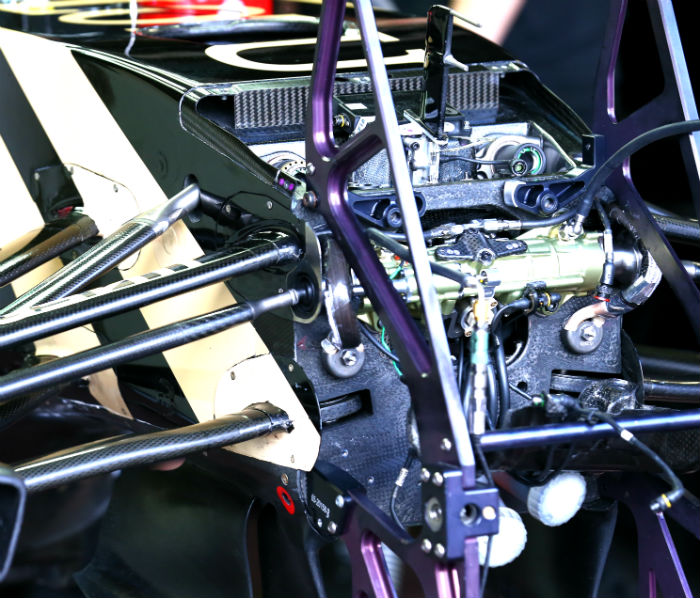
The RS16 uses a hastily adapted E23 transmission which was originally designed for a Mercedes power unit and not the very different Renault RS34 derived RE16 unit.

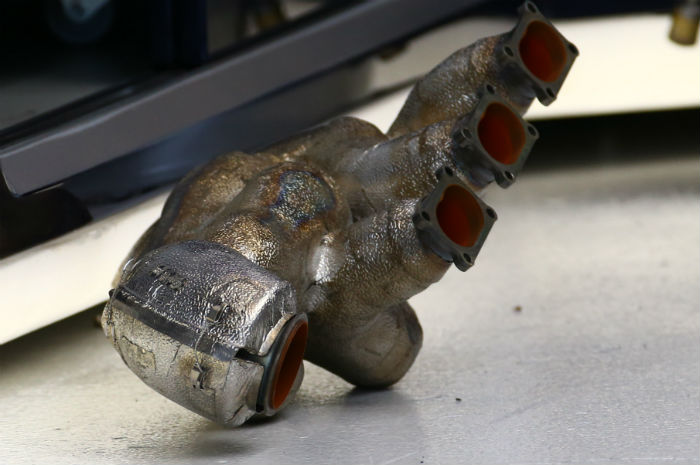
The RE16 exhaust header with its substantial heat shielding (here seen of the floor of the Red Bull garage). These components are part of the homologation perimeter and supplied by the manufacturer.

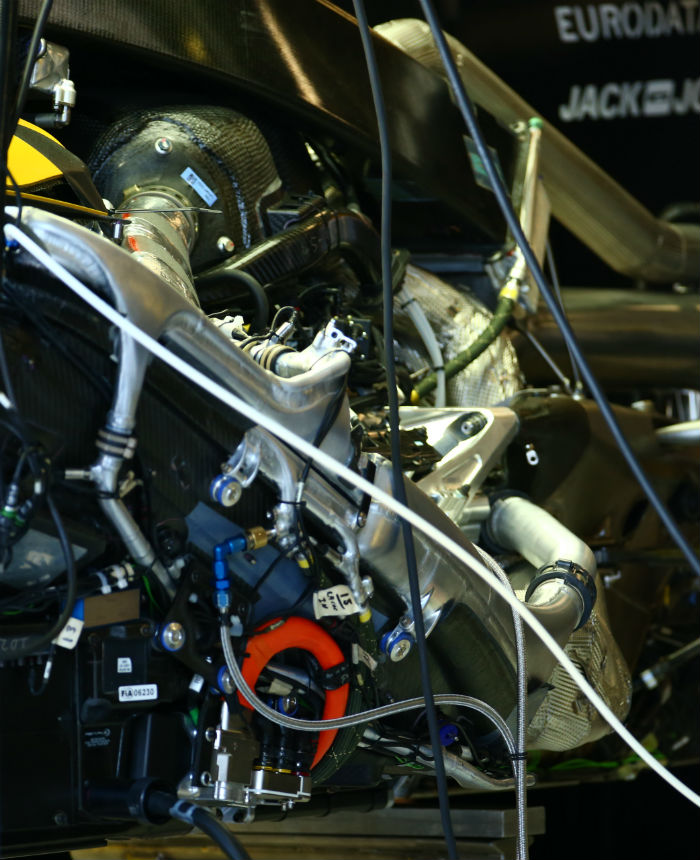
Another, better, look at the installation of the Renault power unit installed in the RS16.

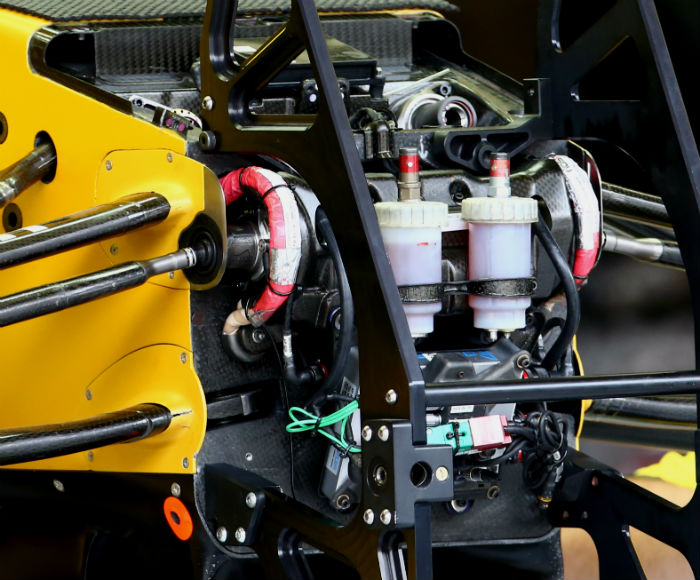
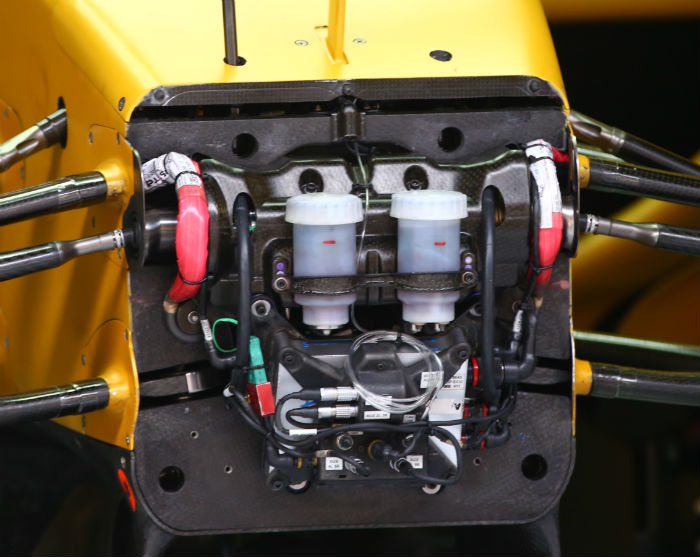
The front bulkhead of the RS16, the wheel tethers can be seen here (red cables), as can the master cylinders and torsion bars.
A look at the rear face of the Renault nose, note the V section at the base behind the front ‘thumb’.
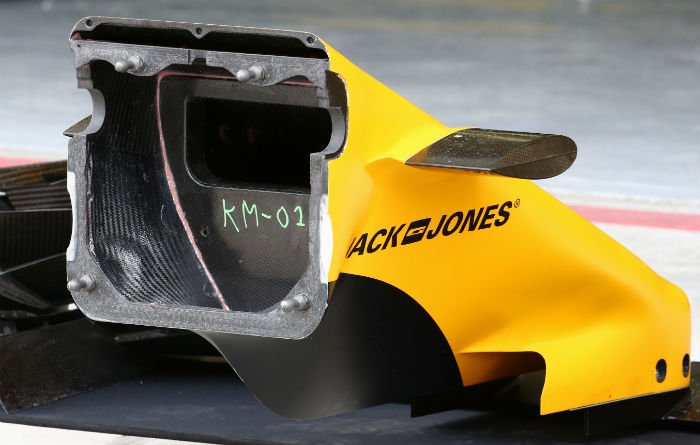

The volume under the sidepod duct contains the usual array of control boxes, hybrid system components. The side impact structure and its mounting to the tub can be seen.
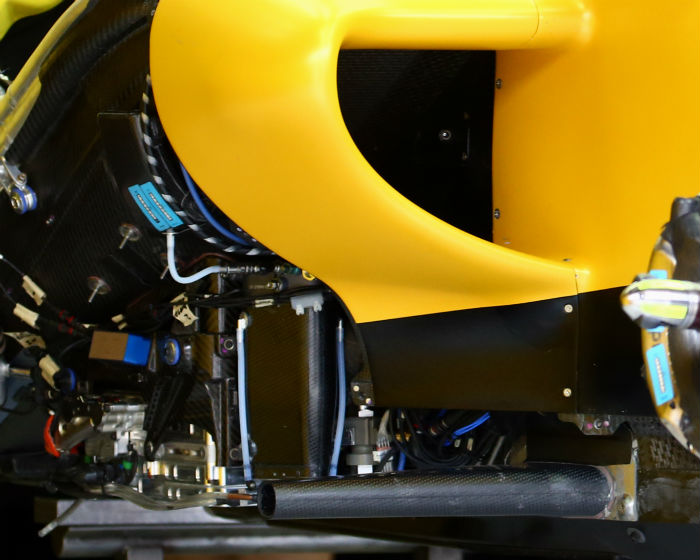

The wastegate exit pipe of the RE16 in Renault (rather than Red Bull) trim is quite large and travels upwards from the wastegate and over some cooling ducting to the rear of the car.
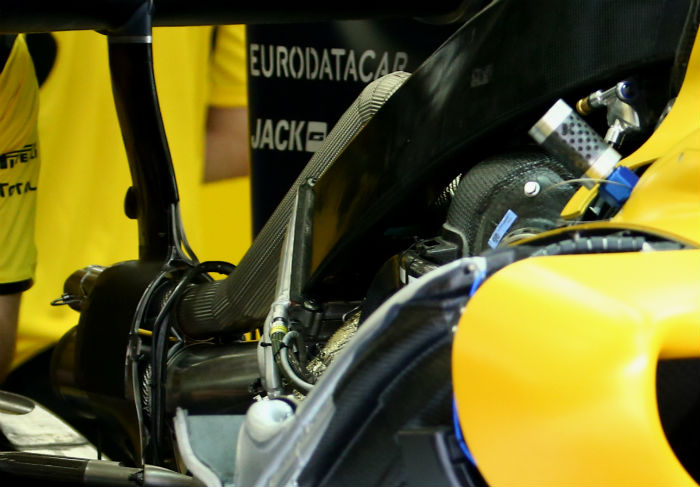

A look at the left hand sidepod of the RS16 with the bodywork removed. Some of the cooler layout is visible including what appears to be part of the charge air cooling system.
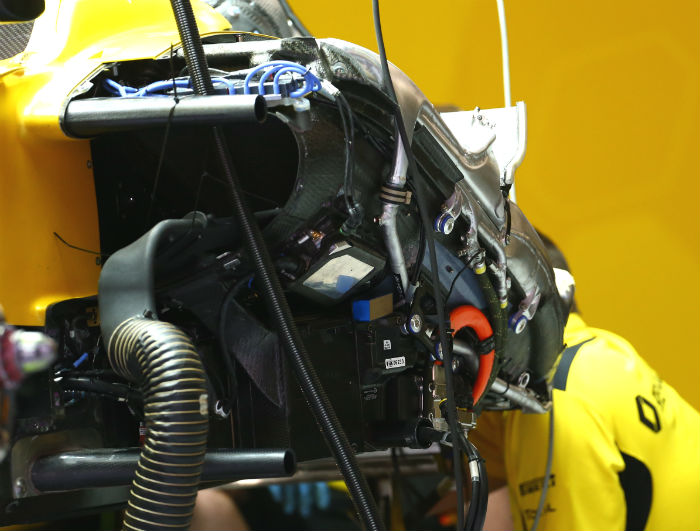

Note the orange electrical cable, it is coloured orange to indicate that it is part of the high voltage circuit of the hybrid system.
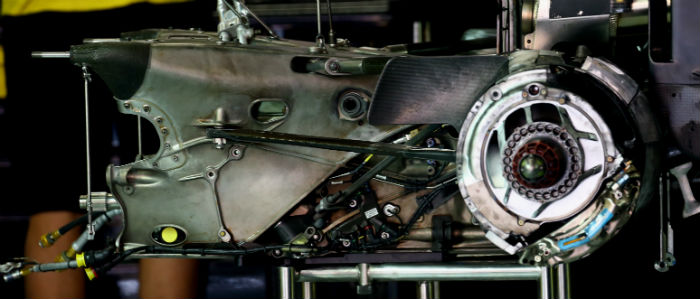
A look at the Renault RS16 system transmission. Due to the last minute switch from Mercedes to Renault power the gearbox had to be rapidly adapted, but it was a task not made too difficult as the E23 gearbox itself was based on that of the Renault powered E22. Compare the E23 transmission (below) to the RS16 design (above). Note how the 2016 unit has a cut out at the leading edge. It is possible to adapt a 2015 casting to 2016 spec according to the team.
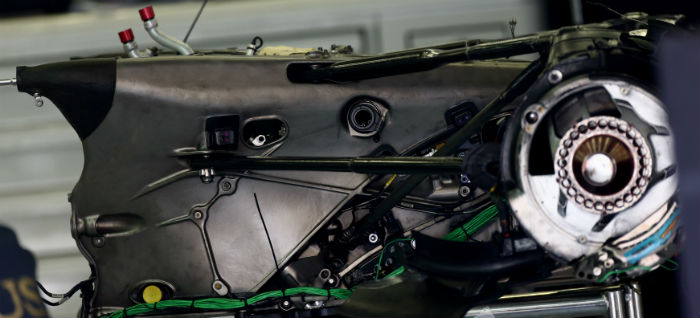
The RS16 has a single wastegate exit pipe mounted above the main tailpipe. Here we get an unusual view of it from the front of the car with the engine side pipe removed.
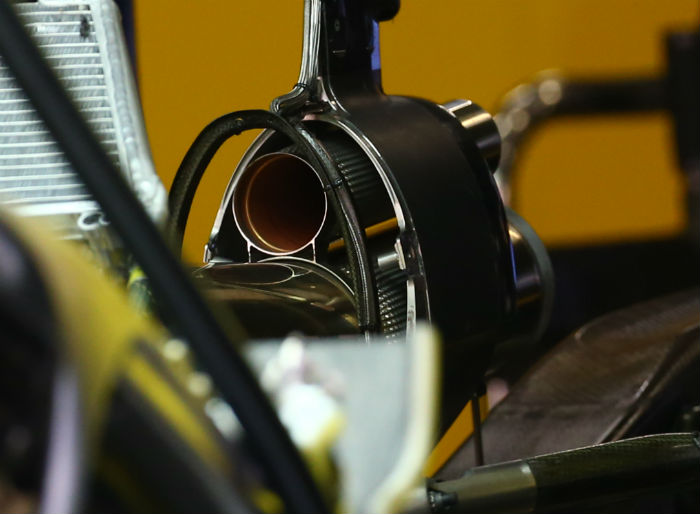

Another look at the front bulkhead of the RS16 (below) with all of the usual components visible, many of which like the steering rack carry over from the E23.
Here is a really unusual view of the Renault rear wing with the end plates absent. While the main wing only has two wing sections, the small link area has four seperate components each with a wing section. It seems that these are all machined from the same single metal billet. Note the DRS actuator.
The Renault being based on an older design is perhaps not as competitive as other cars but at its core there is a notably improved power unit, the RE16
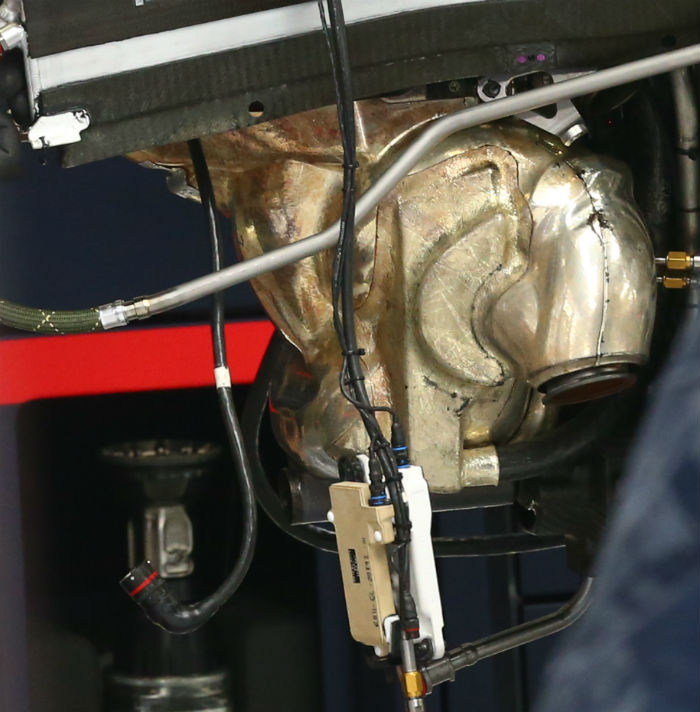
A look at the Renault RE16 V6 engine with the exhaust removed. The oil tank is clear to see as are the two high voltage cables (orange) linking the energy store (battery pack) to the MGU-H and MGU-K
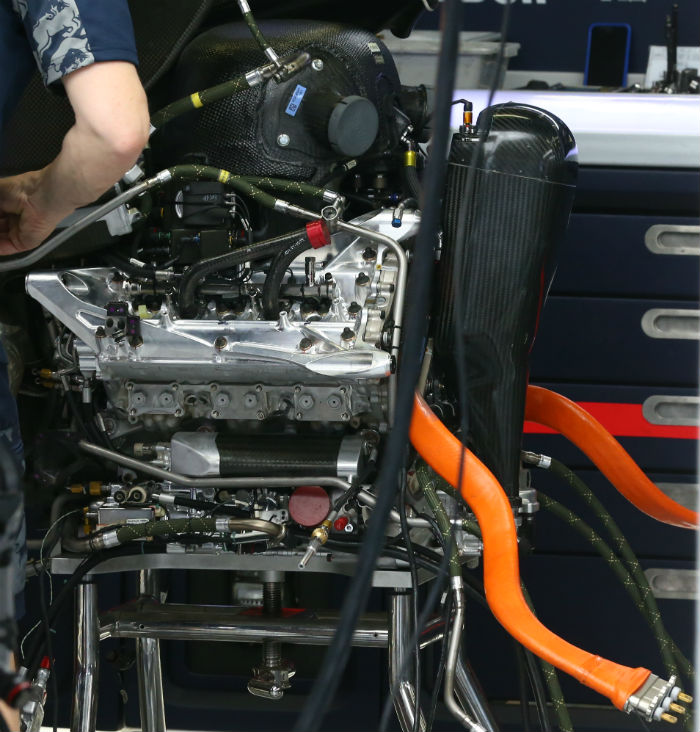
Another look at the RE16 installation, note the canted heat exchanger a carry over from the E23.
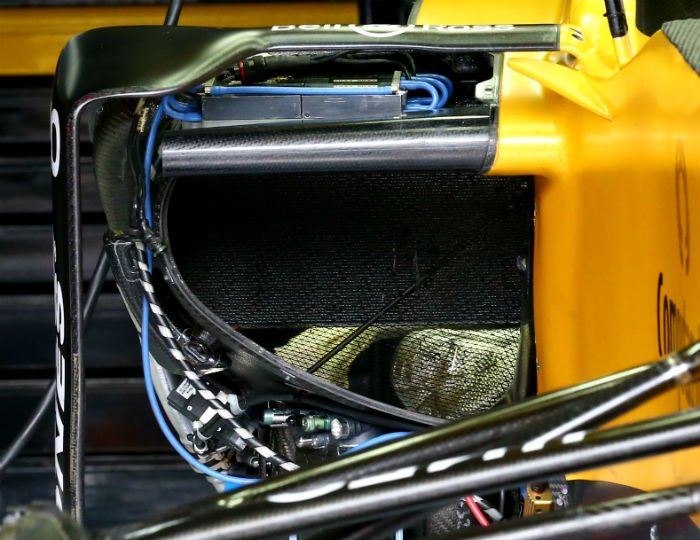

With some bodywork removed as well as some the heat exchangers its possible to see the exhaust position in relation to the main sidepod duct.
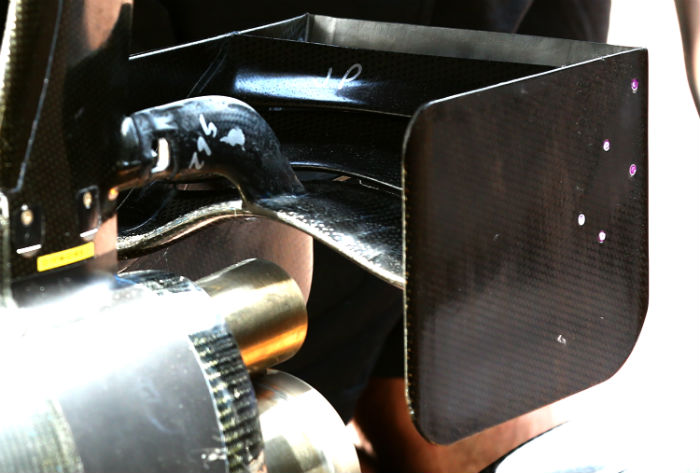

At some circuits the Renault is fitted with an additional winglet mounted on the central pylon. Note how the underside has a thermal barrier applied to the surface, possibly from the Zircoflex range.
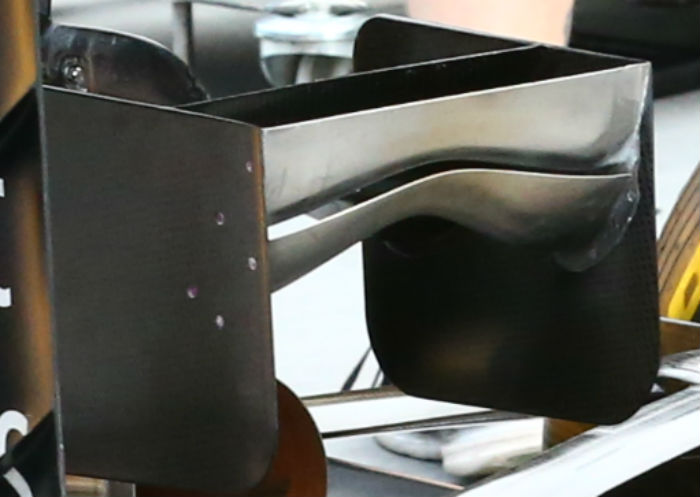

Renault has yet to develop a blended lower wishbone but admits it is working on one for the car.

An unusual look at the rear of the RS16’s floor.

A fire on one of the two Renault’s in Malaysia is thought to have been caused by the failure of a new fuel system component. Exactly what failed is not clear but it is thought to be in the region of the main fuel pump.
“Kevin’s car had a fuel breather issue in FP1 resulting in the ignition of escaped fuel. He missed most of the session as the car was cleaned and repaired from the extinguisher chemicals” Renault’s official statement read.
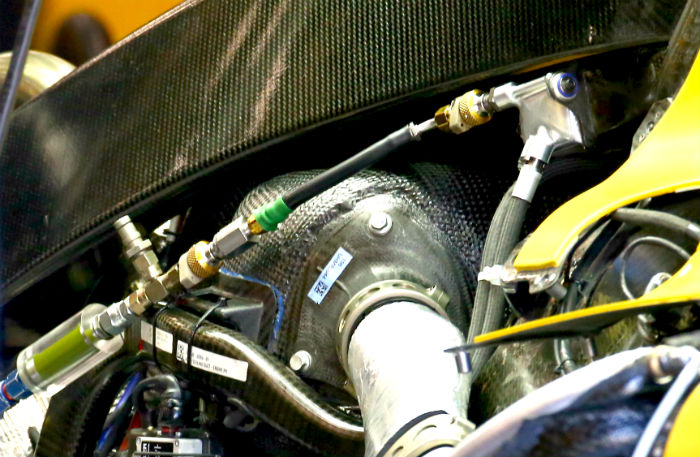

Looking at this image of the area where the component failed a fuel line can be seen entering what appears to be a cooler fed by ducting around the roll hoop. It is here where the fuel (under pressure) was leaking from. In the picture above the car is connected to a hose from equipment in the garage – likely the fuel bowser, note the in line fuel filter.
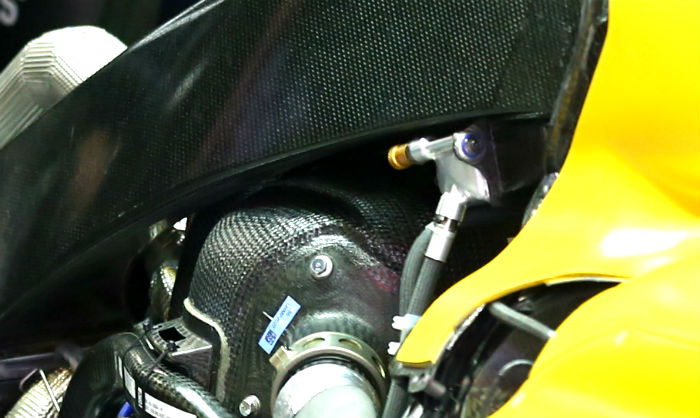

In the image above however the cooler can be seen in race setup with the vent hose removed, note the small copper coloured fitting (a fluid connector) – this may be the component that failed allowing fuel to leak out from such a high position on the car.

A late season update in Asia saw the RS16 fitted with new tighter sidepods, compare the original specification (below) with the new version (above). Its likely that these reworked sidepods were introduced with a number of under the skin packaging improvements.

THE RENAULT RS16 IS FEATURED IN A SPECIAL 10 PAGE ARTICLE IN RACECAR ENGINEERING MAGAZINE – READ IT NOW BY CLICKING THIS LINK~




