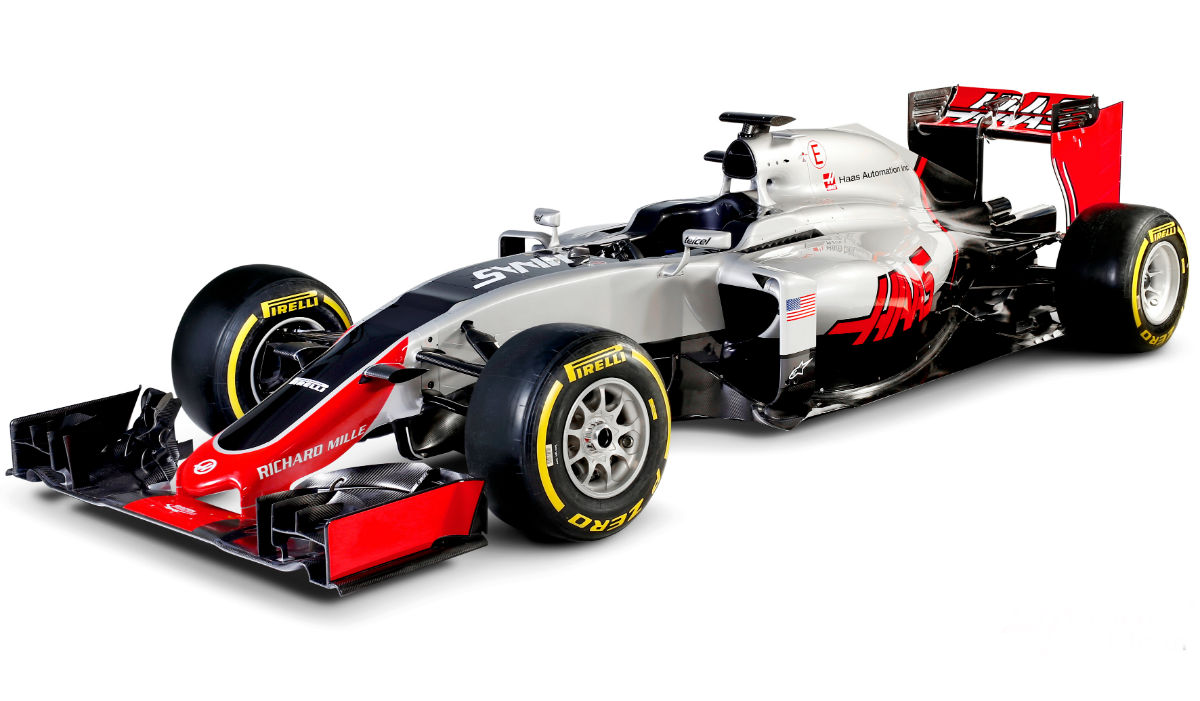
The Haas VF-16 is the first car from the US based team, but it has largely been constructed in Italy.
In the past to be considered a constructor a team would have to design an construct its own chassis, front impact structure, suspension, suspension geometry, radiators, bodywork, steering system, brakes, floor and fuel tank at the very minimum. But at the start of the 2014 season that requirement was dropped to only require teams to design and build the chassis, front impact structure, suspension, suspension geometry, brake ducts and bodywork. For 2015 that has been further simplified again an now a constructor only needs to make the monocoque and bodywork. Everything else can be purchased.
Haas opted to have Dallara manufacture the chassis for the VF-16, while Ferrari will provide almost everything else. “We have the front suspension, rear suspension, hydraulics, steering, electronics all from Ferrari. Radiators we have to do as that is classified as bodywork” Steiner explains. “We are using these things to focus on the overall car design, why make an effort to do our own damper or something when we can just get them from Ferrari.. We have everything exactly the same as the Ferrari.”

The overall design of the Haas is very conventional, with front pushrod suspension, pull rod rear, and most of the major systems as conventional. To the point where one observer in the pit lane at Barcelona suggested that the VF-16 was the ‘default 2016 F1 car’.
Haas and Ferrari shared a substantial amount of aerodynamic data with Ferrari during 2015 and as a result there is no surprise that it appears to be generally similar in concept to the Italian car, but very different in detail. To say that Ferrari did everything on the Haas is too far, Ferrari was blocked from the data sharing in late 2015 and Haas for a long time had its own CFD team augmenting the Italian operation.
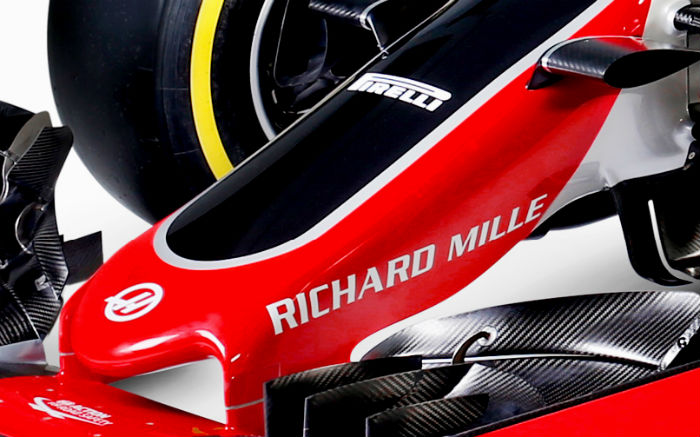

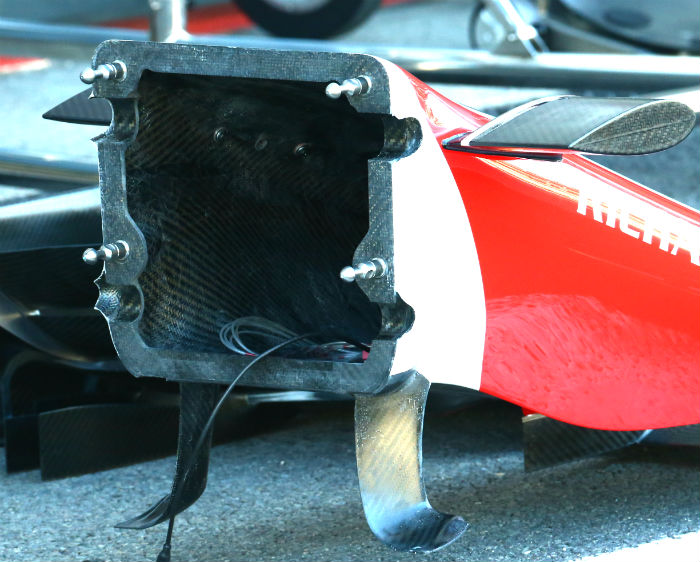
The nose of the Haas is similar in concept to the Ferrari with a protruding front impact structure but this seems smaller than that of the SF16-H or the 2015 Sauber.
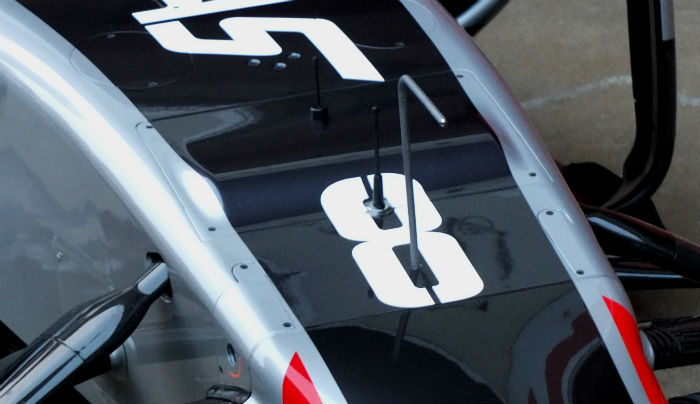

Higher up the nose there is a hump which almost certainly accommodates some suspension components. It is strange that Ferrari was able to accommodate these but Dallara was not. It will be interesting to see this region with the panels removed.
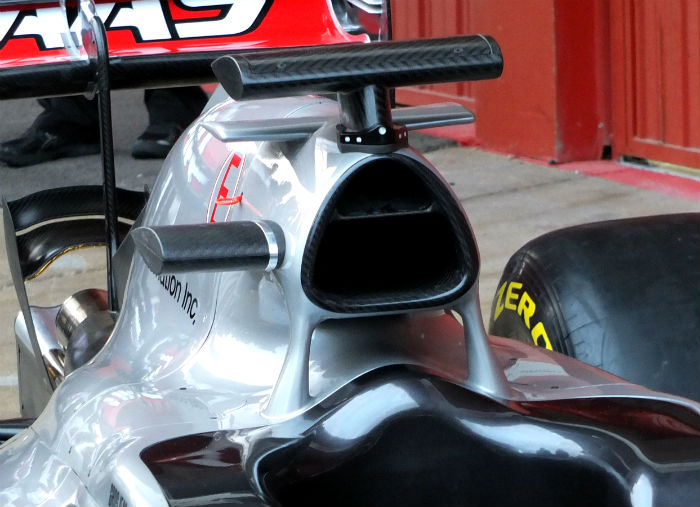

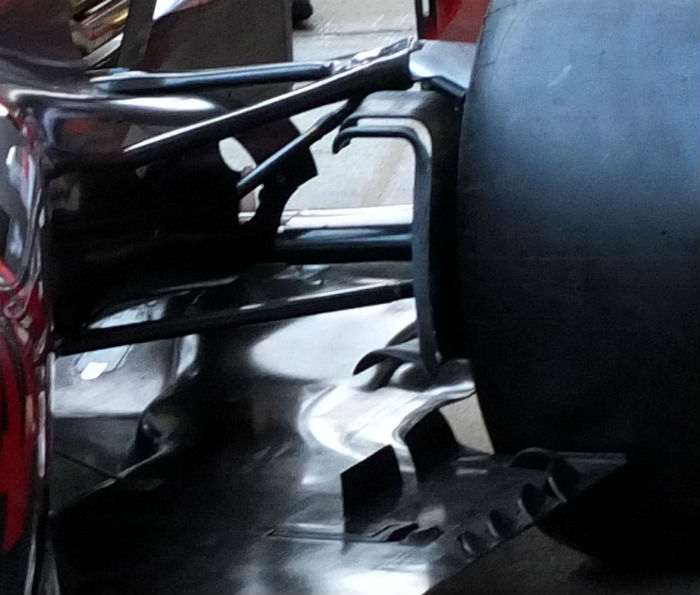
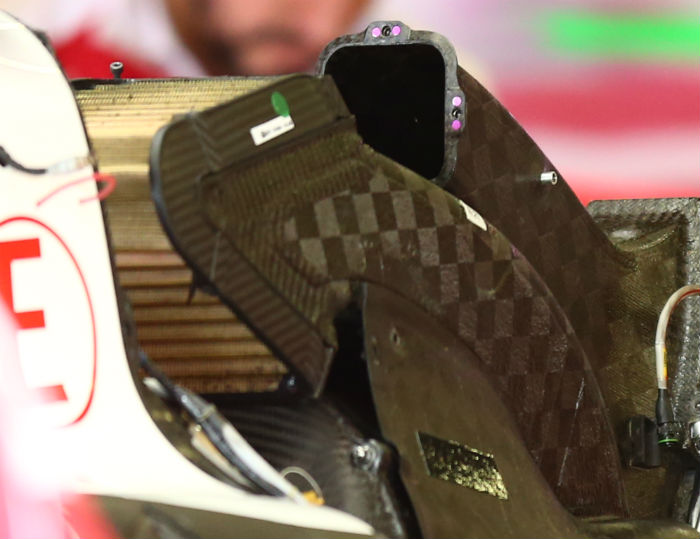
The roll hoop is more conventional than the SF16-H with two forward supports and is a Dallara element rather than a Ferrari one (Dallara used similar supports on the HRT F110). The supports are sculpted and have clearly undergone significant optimisation work. The airbox itself is split in to two similar in style to the McLaren layout with the lower segment feeding the Ferrari V6 combustion air while the upper segment supplies a cooler positioned around the bell housing area. There is also a very small cooling duct under the main hoop as is conventional with the current generation of cars.
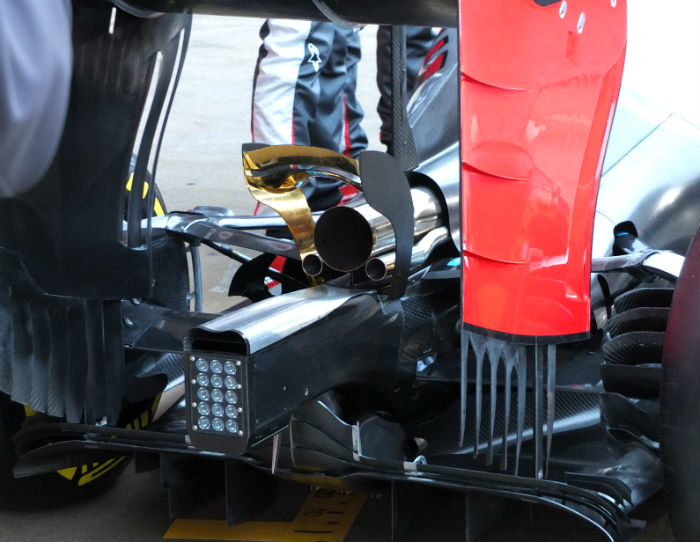
Here is a good look at the rear of the car, note the twin wastegate exist either side of the tailpipe. The ‘monkey seat’ winglet has a gold thermal barrier (possibly Zircoflex Gold) applied to protect it from the exhaust heat. Not clear in this or any images seen yet is whether the rear wing support passes through the tailpipe but it seems that it does. The rear wing endplate features a slot on the leading edge and a number of strakes, at the base there is the now standard feathered base.
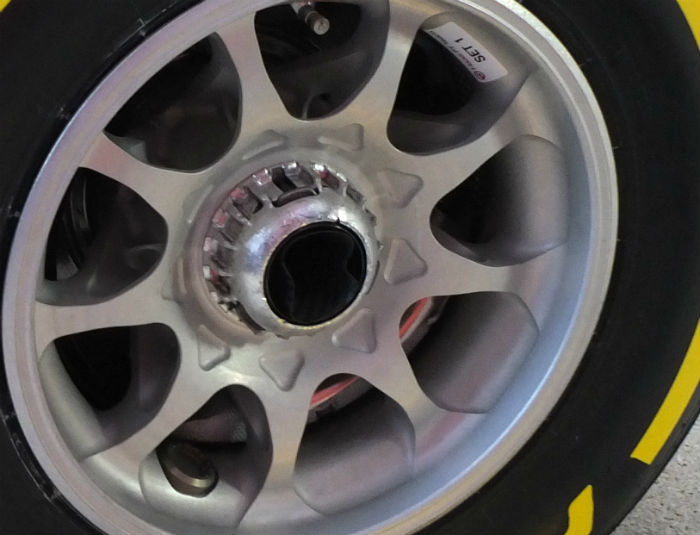

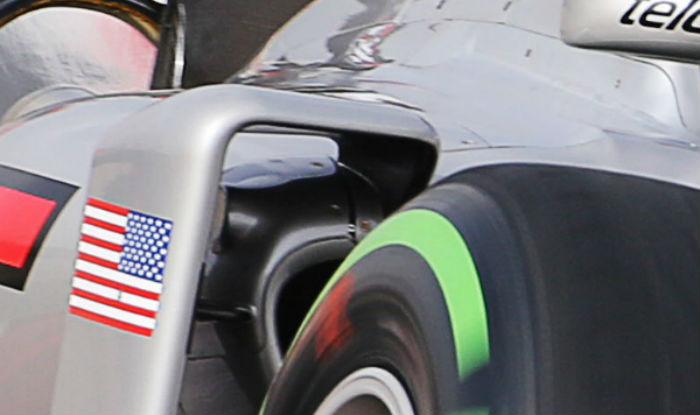
The front wheels/uprights of the VF-16 feature so called ‘blown’ wheel nuts, with a channel through the centre.
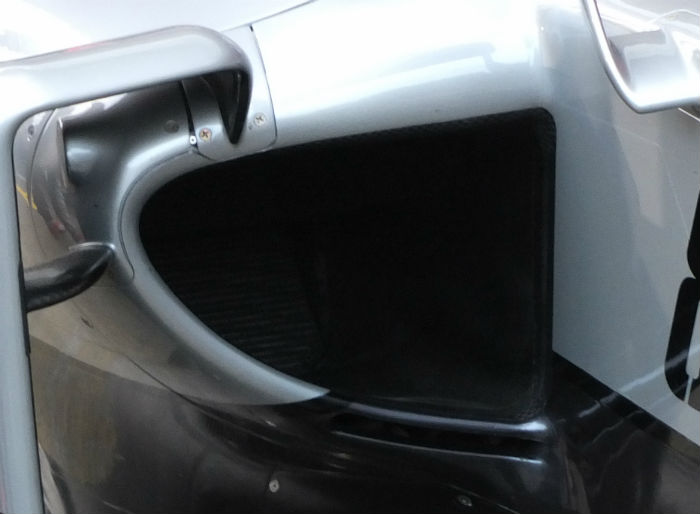

The sidepod duct on the VF-16 is fairly conventional (the cooler is just visible in this image), a small slot under the main duct likely cools some electronic components mounted under the bodywork in this area. A small bulge on the outer edge of the sidepod is visible, this is the out extremity of the mandatory side impact structure.
Comparing the VF-16 to the Ferrari SF16-H is an interesting exercise, the front wing is essentially identical on both designs –
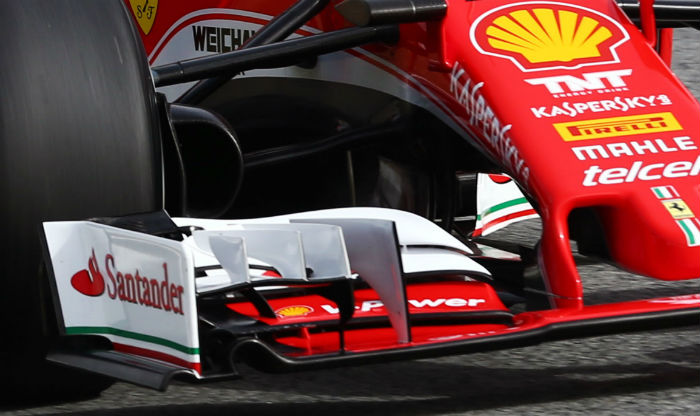

compare the Ferrari (above) to the Haas (below) the brake duct design is also identical as are the wishbones. The nose concept differs however between the two cars.
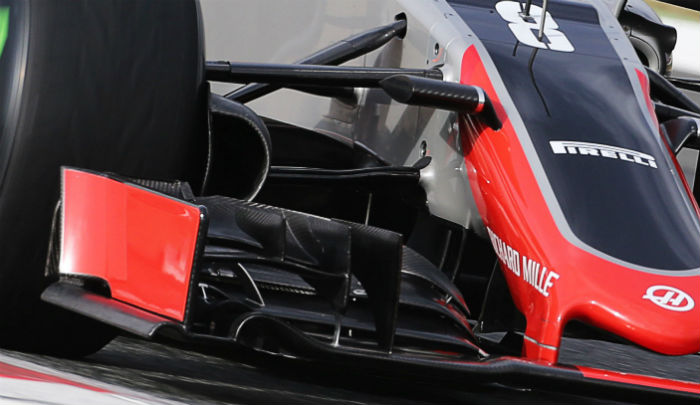

The rear suspension is basically identical between the two cars including the ducts, wishbones, uprights, but the Ferrari has a slightly more complex treatment on its floor (not pictured).
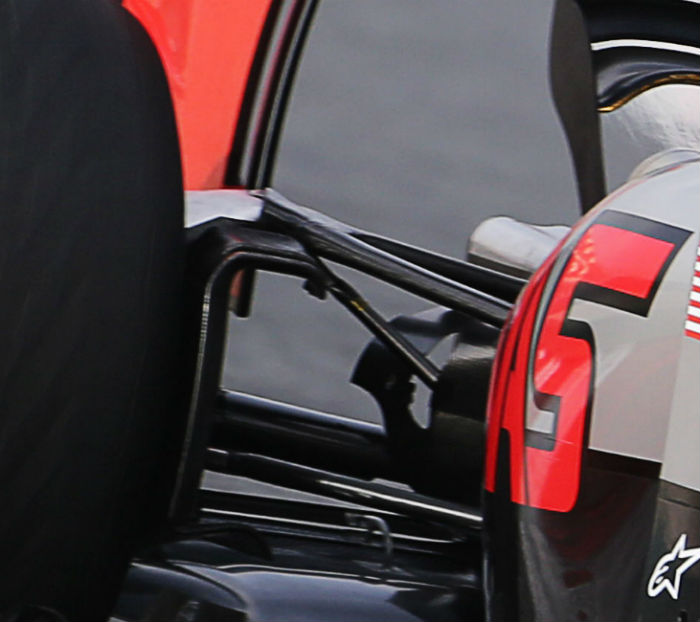

Ferrari (above) and Haas (below) component sharing is the closest Formula 1 has come to customer cars since the Super Aguri team folded but is allowed under new rules introduced at the start of the 2015 season.
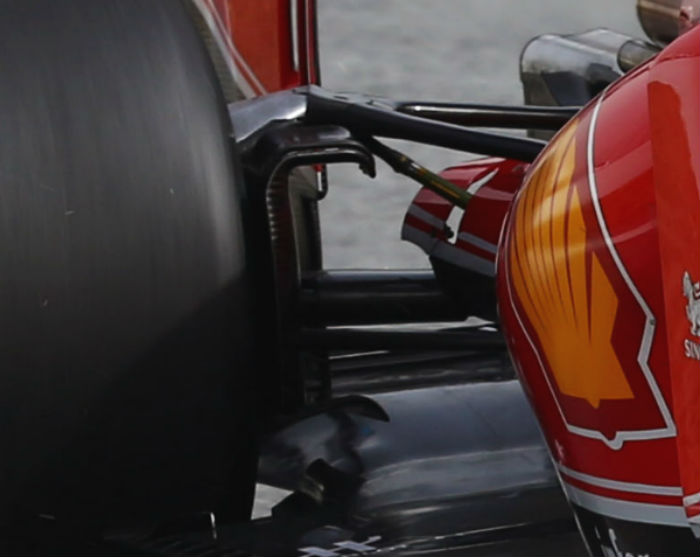

At the rear of the car there are similarities but also differences, while both cars share rear impact structures and transmission there are some detail changes between the two.

Looking at the rear wing it is largely identical between the two (Ferrari above, Haas below) but note that the rear wing support does differ.

Finally some areas of the car share a general concept but are entirely different designs, the cooling system on the Haas by regulation is bespoke to that design, but looking at the sidepods the impact of the data sharing can be seen.

The Ferrari, above has a very similar treatment in terms of the turning vane around the outer edge of the sidepod and the small bump caused by the protruded side impact structure.

The Haas and Ferrari share an overall diffuser design but there are some subtle differences between them.

In the centre section under the rear impact structure the Ferrari diffuser (above) is dead straight while the Haas variant (below) dips down slightly. On the outboard edges both versions feature a stack of four small elements, but the Ferrari versions are rather more angular. The base of the Ferrari rear wing endplate features a set of horizontal louvres where the Haas has nothing at all.

Below is another look at the roll hoop and airbox design on the Haas, the under hoop cooling duct is just visible.
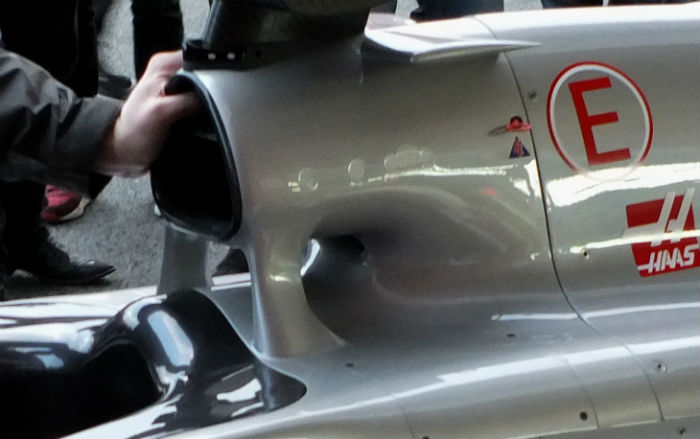

After a slight mishap involving an unexpected detachment of the the frontal aerodynamic assembly (the front fell off) the Haas team made a temporary fix.
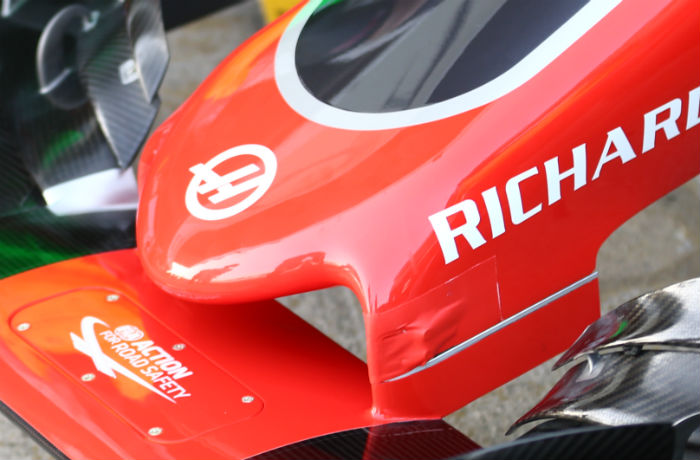

The Dallara built Haas chassis follows a trend started by the Marussia MR03 by utilising an aluminium front bulkhead, something which is claimed to offer a bit more design freedom.
A look at the front edge of the side pod on the VF-16 note the additional cooling slot under the main duct.
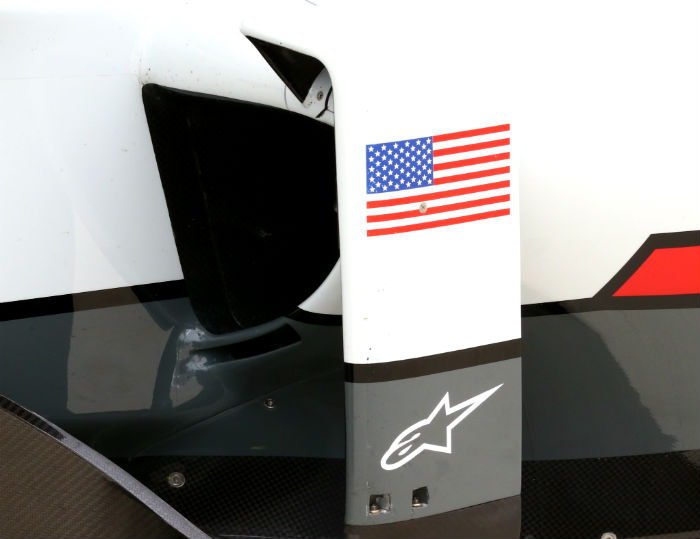

Under the skin of the sidepod the usual side impact structure is visible as is the array of electrical control boxes and some hydraulic actuators.
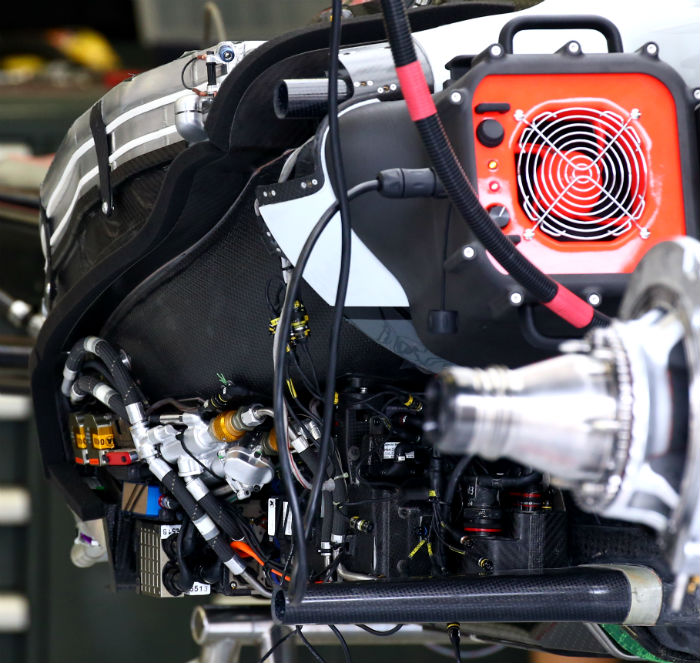
Here we get a look at the Ferrari power unit installation of the VF-16. In this image the wastegate is removed and the turbine end of the additional exit pipes can be seen.
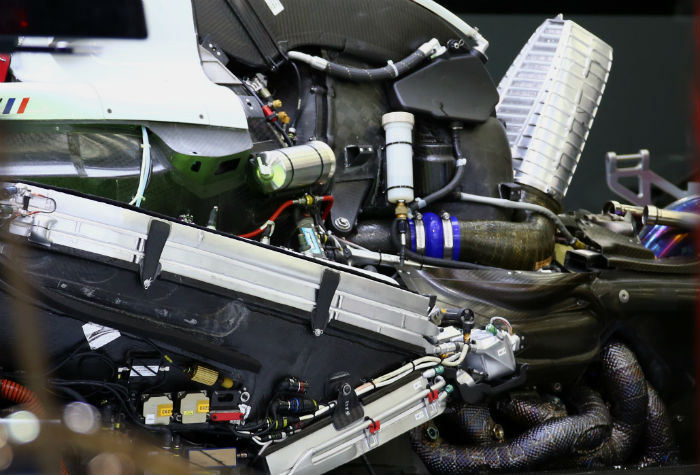

Below them the exhaust layout can be seen with the pipes coiling their way into the bellhousing where the collector is located, this is a very hot and very crowded area of the car. The sideways V shape of the radiators on the car is by regulation Haas and Dallara’s own work but none the less is a very similar layout to the Ferrar SF16-H
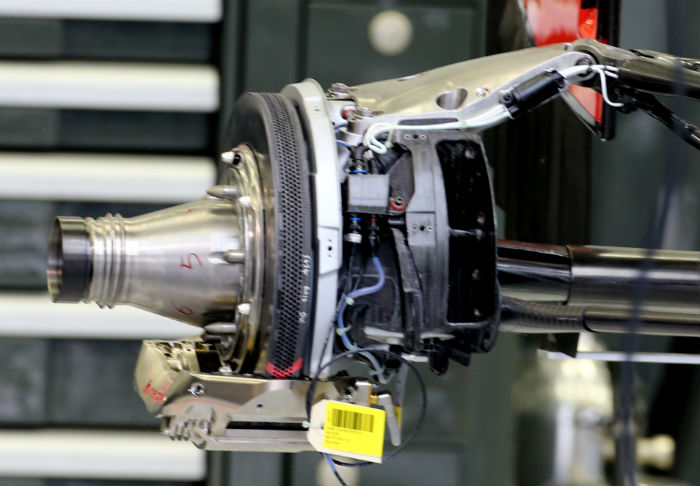
A look at the rear upright of the Haas (and the Ferrari VF16-H), note the size of the upper extension, and the Brembo caliper located at the base of the disc.
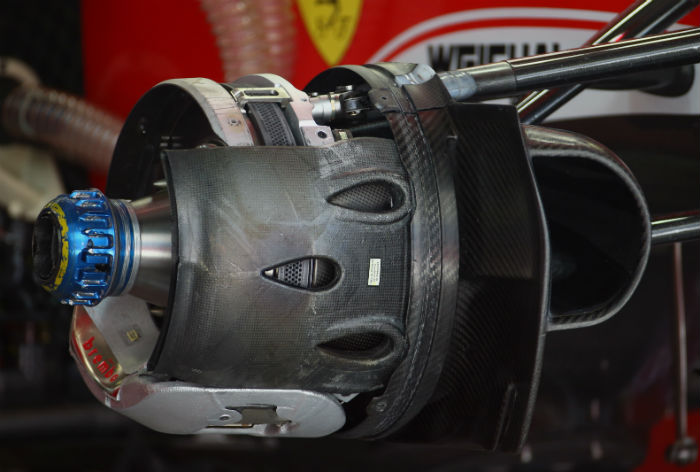
This page mas made many comparisons between the Haas VF-16 and the Ferrari SF16-H which is very closely related to it in mechanical terms. For example the two cars share their uprights and braking system, as you can see comparing the two (Ferrari above, Haas below).
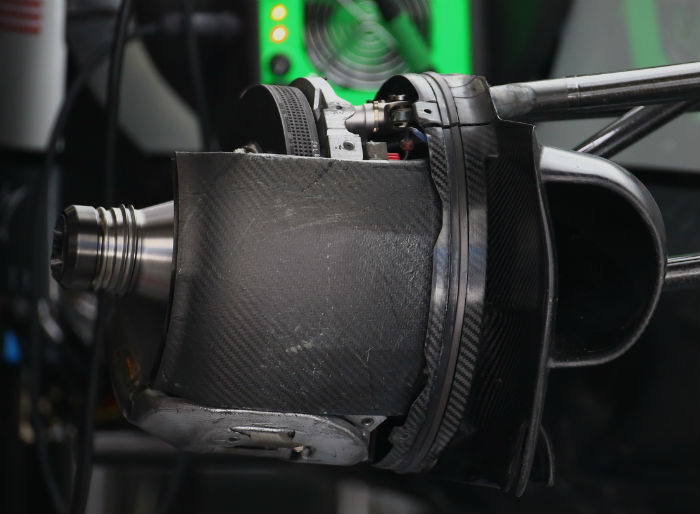
Interestingly it appears that the internal ducting varies a bit, with the Ferrari design featuring its three distinctive tear drop openings far more complex than the Haas design. Note how the Ferrari supplied part has the dimples to accommodate the teardrop duct on the Haas but the US branded (and funded) Italian built car does not use them.
The brakes on the Haas have been a cause for concern for a lot of the season, as its drivers struggled with them on many tracks. Its not quite clear why this has been the case as most of the components used by Haas are identical to that used by Ferrari – which has not suffered similar issues.
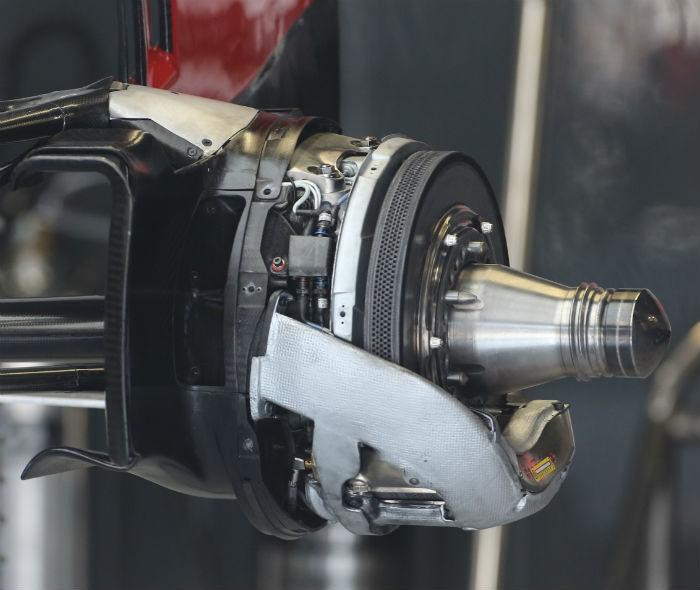
(A look at the rear brakes on the Haas – essentially identical to those used by Ferrari)
In the latter part of the season the team suffered a brake by wire failure and a disc failure, neither of which are issues which have manifested themselves on the seemingly identical Ferrari package. Haas is thought to use Brembo friction material but in Brazil planned to test an alternative supplier.
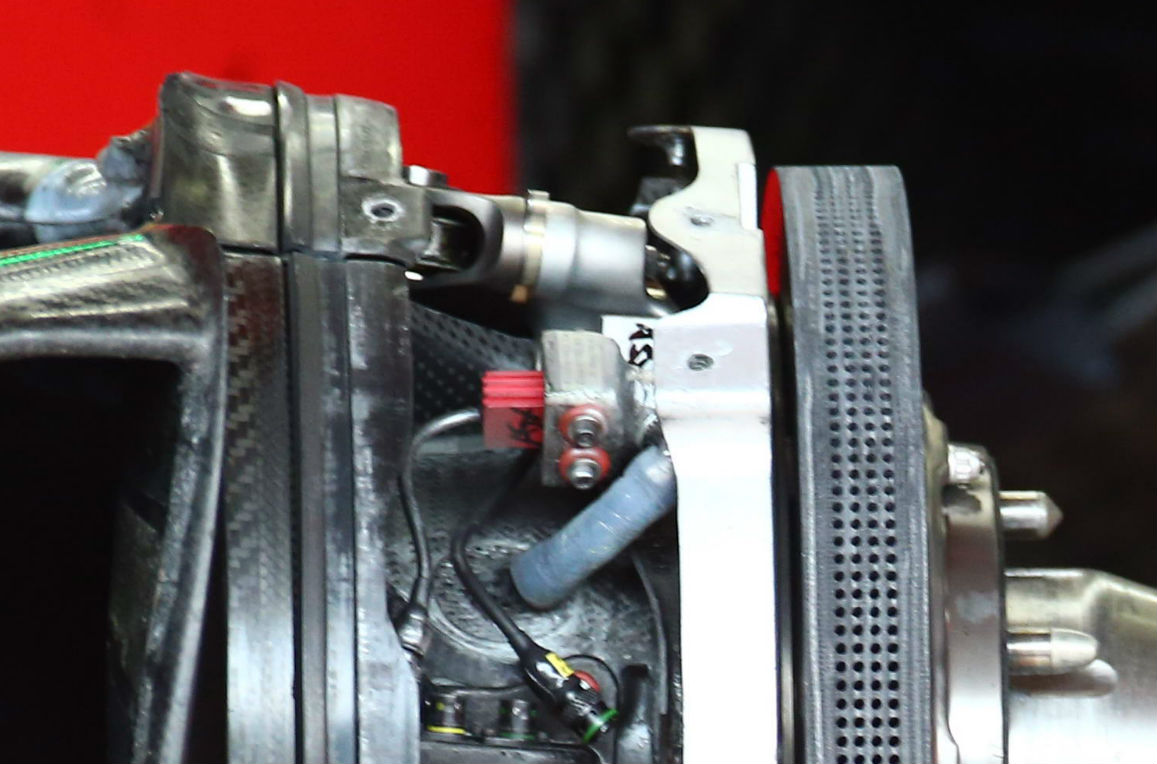
For comparison here is the Ferrari front brake setup (above), note the drilling pattern is identical to that seen on the Haas discs. (below)
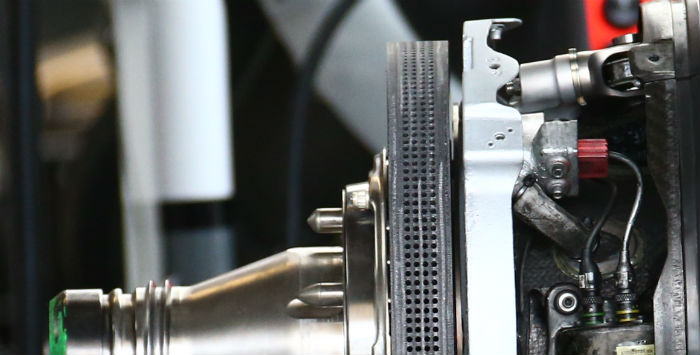
A look at the rear brakes of the Haas – as is the case with the fronts they are essentially identical to those used on the Ferrari.
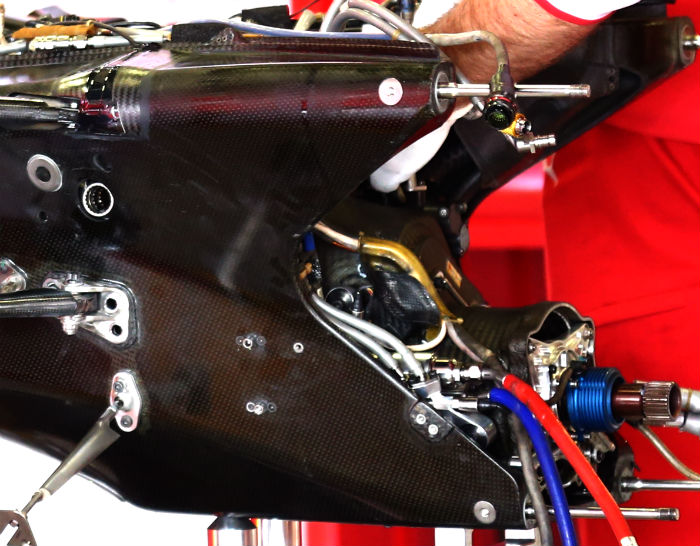
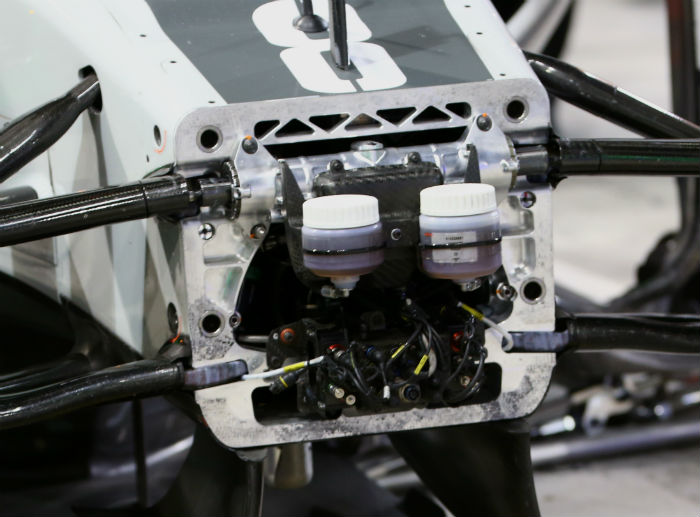
Here we get a glimpse of the front end of the Ferrari transmission, note the internal cover above the input shaft(above).
With a one piece casing the bell housing hosts not only the turbine, hydraulics and rear suspension components, with all of those removed we get a rare look at the front face of the gearbox.
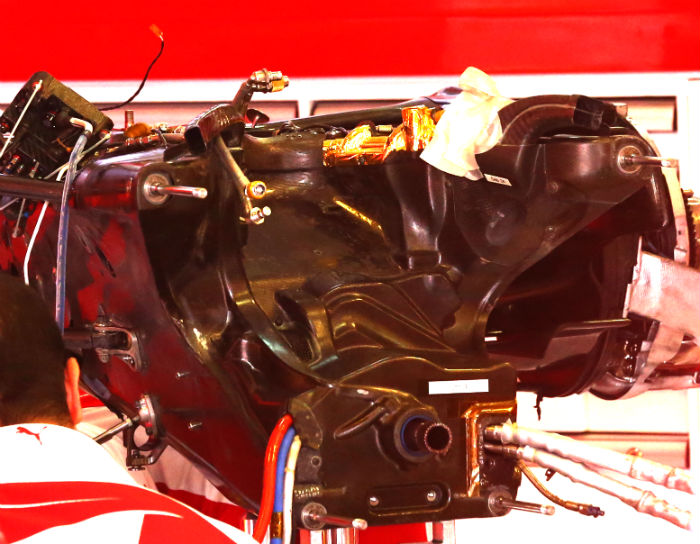
A look at the front end of the Ferrari power unit reveals a charge air cooler at the front of the engine block. The oil tank is on the right hand side of the front of the block.
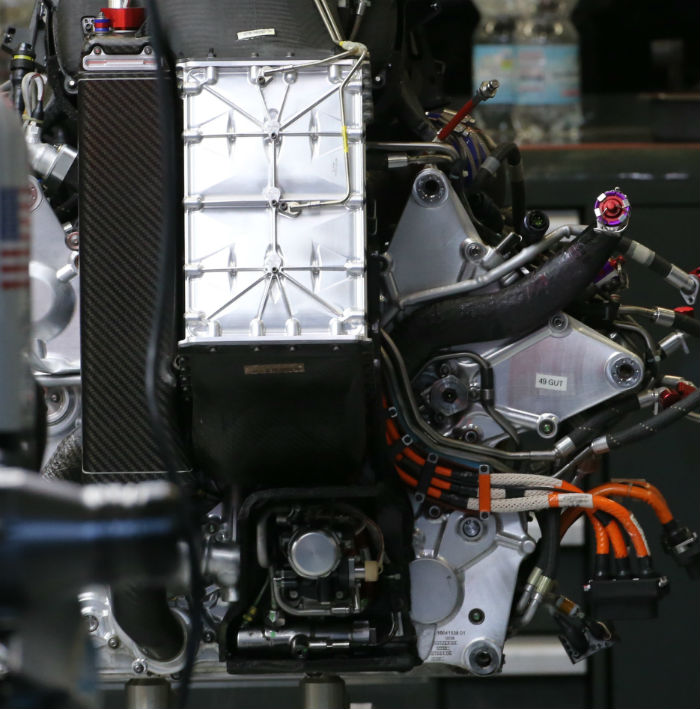
A look at the other side of the power unit with most of its heatshields removed, note the exhaust layout, oil tank and the air filter.
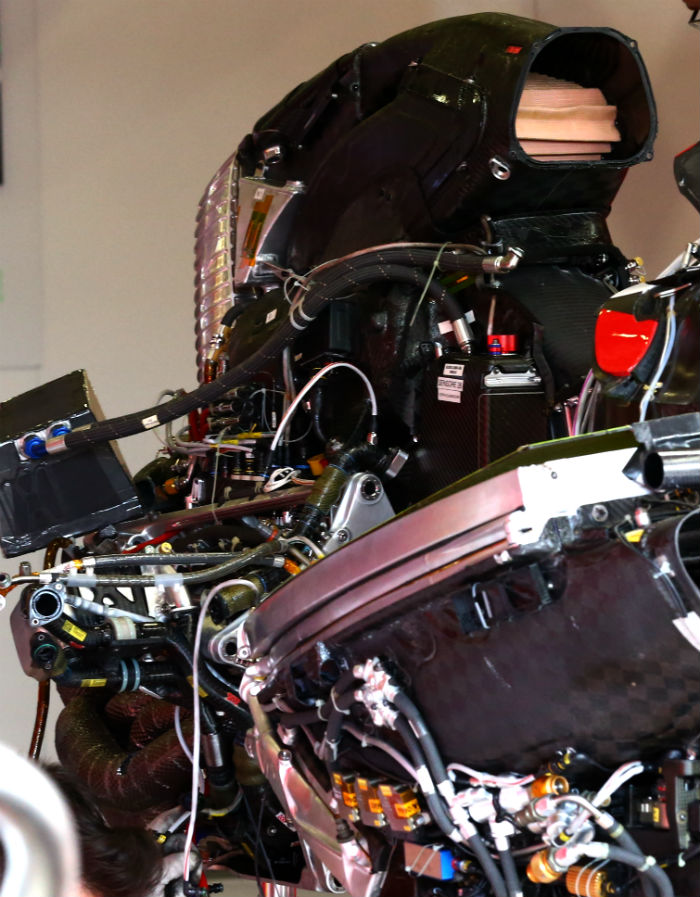

With some of the ducting removed it is possible to see the triangular shape of the air filter on the Ferrari V6.

Note how the oil tank on the Ferrari V6 is squeezed up against part of the charge air cooling system
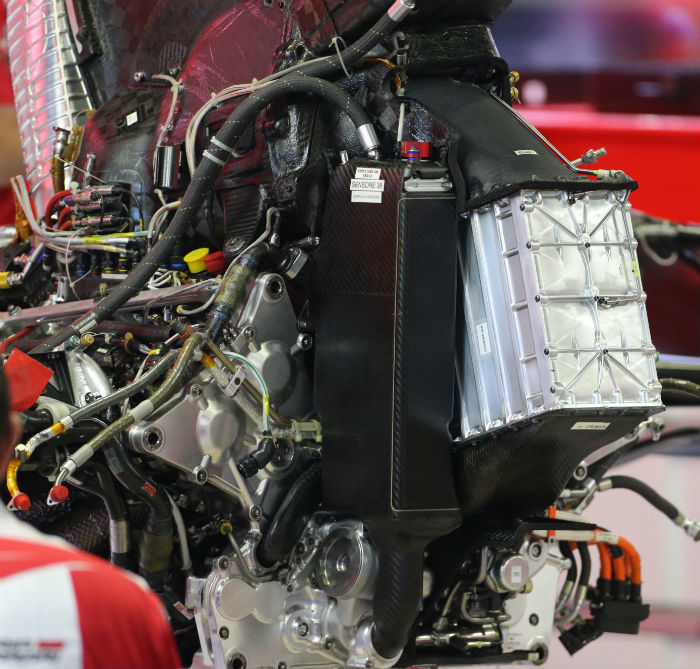
At Monza Haas ran with a special low drag rear wing, it was quickly dubbed the ‘wobbly wing’ not just for its shape but also due to the fact that it was very, very wobbly as the cars hit the kerbs at the three chicanes at the Italian circuit.

It was so extreme that some present were moved to suggest that that degree of lateral flexibility in the wing support was bound to cause a failure bit ultimately it did not.
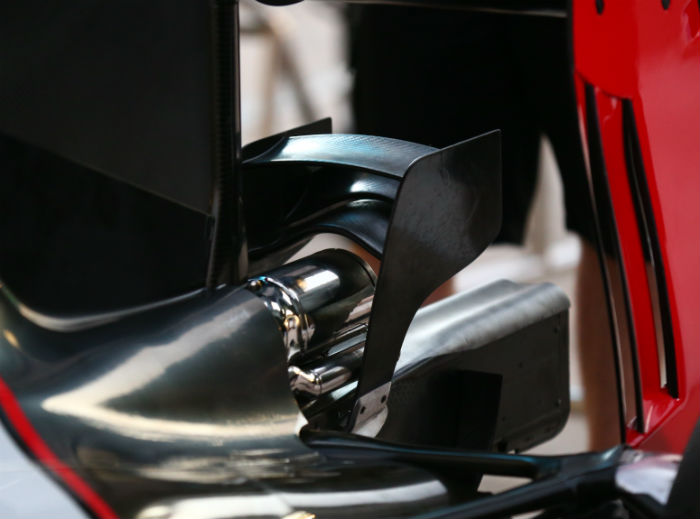

Meanwhile at Austin a few weeks later Haas did suffer a number of rear wing failures, or rather the rear winglet which fell off the car a number of times.
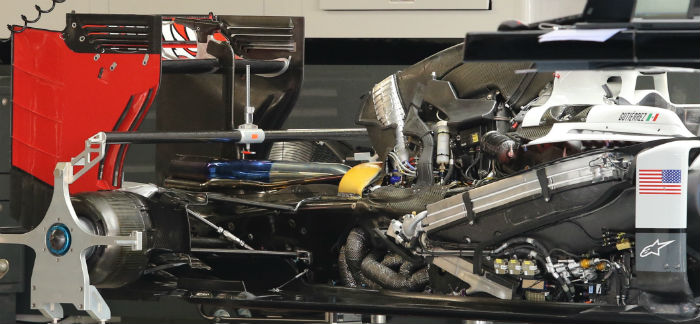
Another look at the Ferrari power unit and transmission in the Haas (above and below).
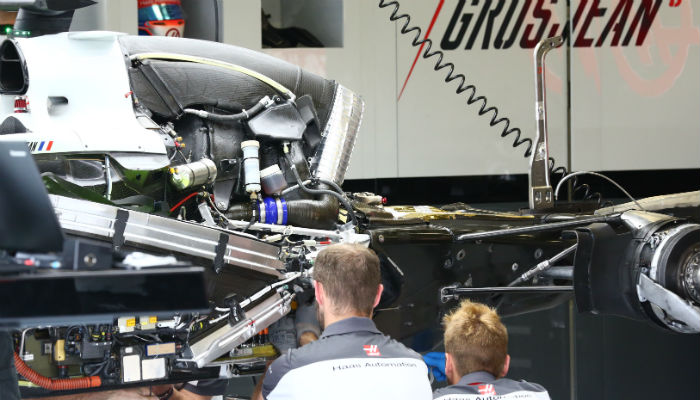
Here we get an unusual look into the Haas nose, this is one of the components of the car which has been made jointly by Haas and Dallara.